A SATA cable itself does not provide power; rather, it’s responsible for data transfer between devices like hard drives, SSDs, and the motherboard. However, the confusion often arises because there are two types of cables involved in SATA connections: SATA data cables and SATA power cables.
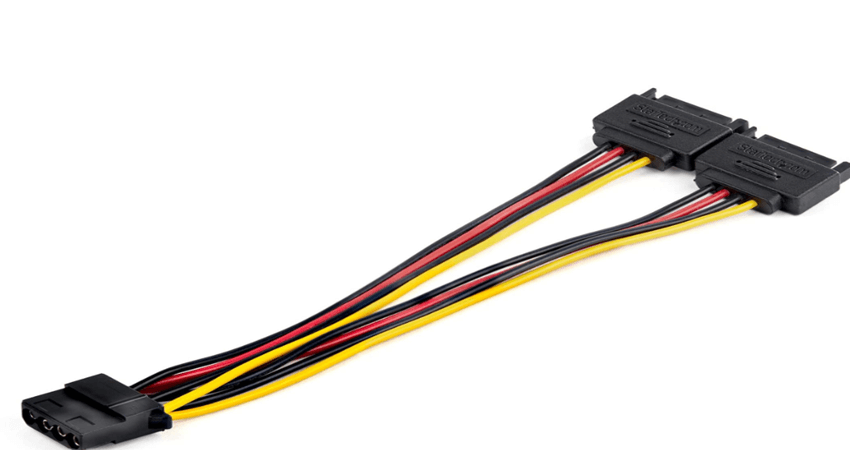
- SATA Data Cable: This slim cable is used solely for transferring data between storage devices and the motherboard. It doesn’t carry any electrical power. Its primary role is to facilitate communication between the drive and the system for read/write operations.
- SATA Power Cable: This is a separate cable that connects the power supply unit (PSU) to the storage device. The SATA power cable delivers the necessary voltage to power the drive. It typically has 15 pins and provides 3.3V, 5V, and 12V power to various components within the storage device.
So, while a SATA connection involves both power and data, it’s essential to understand that the SATA data cable doesn’t supply power. Power comes from the SATA power cable, which directly links the power supply to the drive.
This separation of roles ensures that storage devices receive stable power and fast data transfer without interference.
| Read More Topics |
| How to make a LEGO mindstorm robot? |
| Definition and origin of electrode potential |
| General communication system |