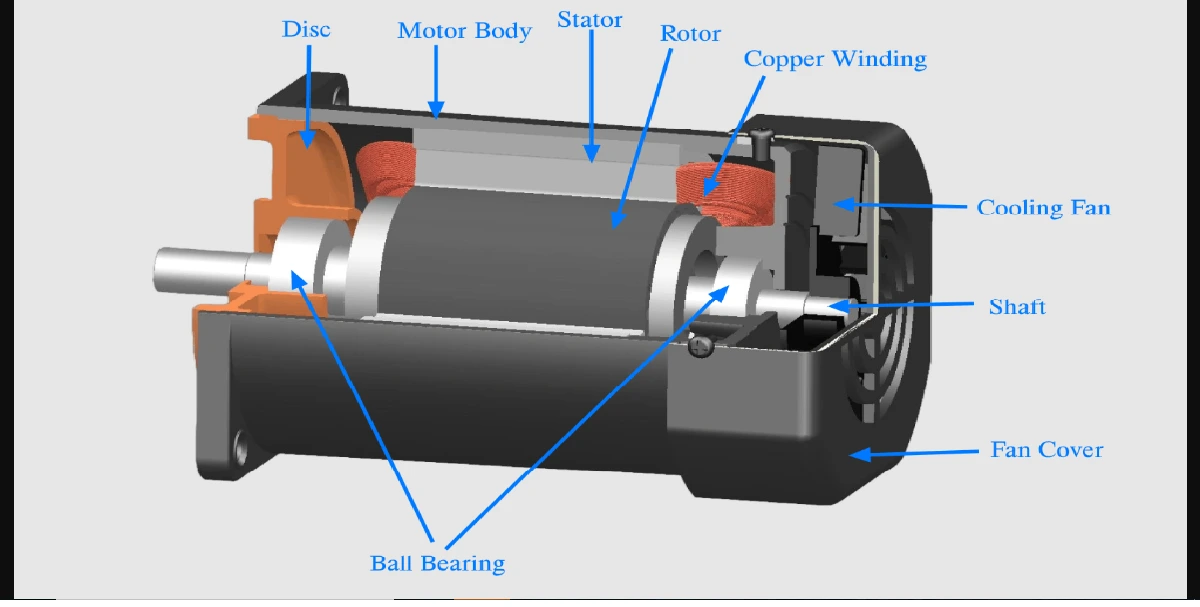
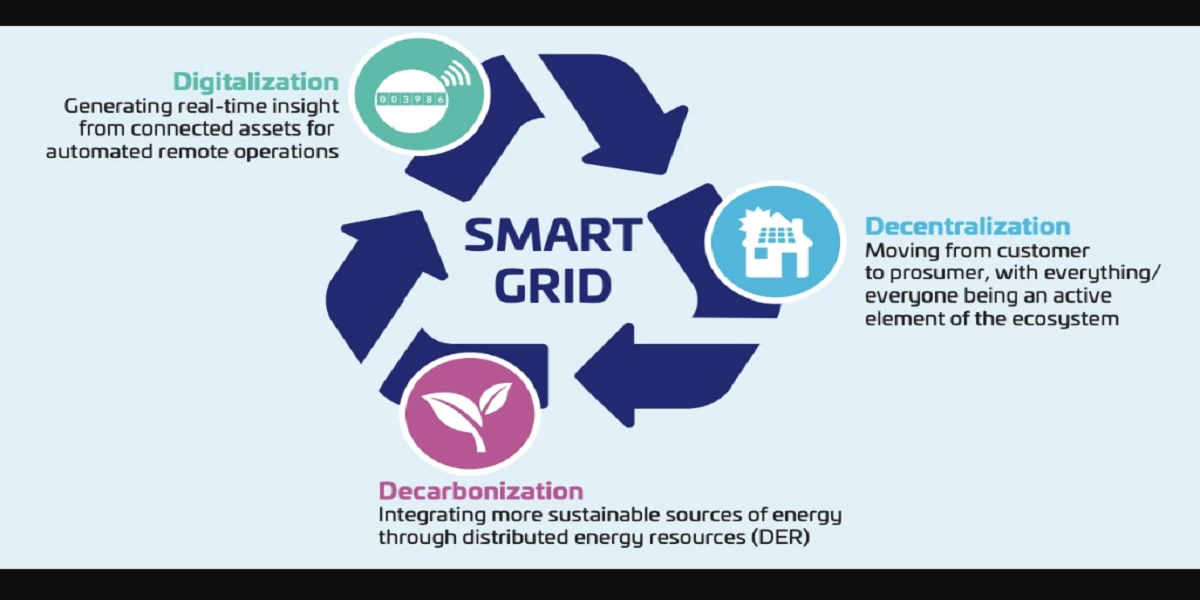
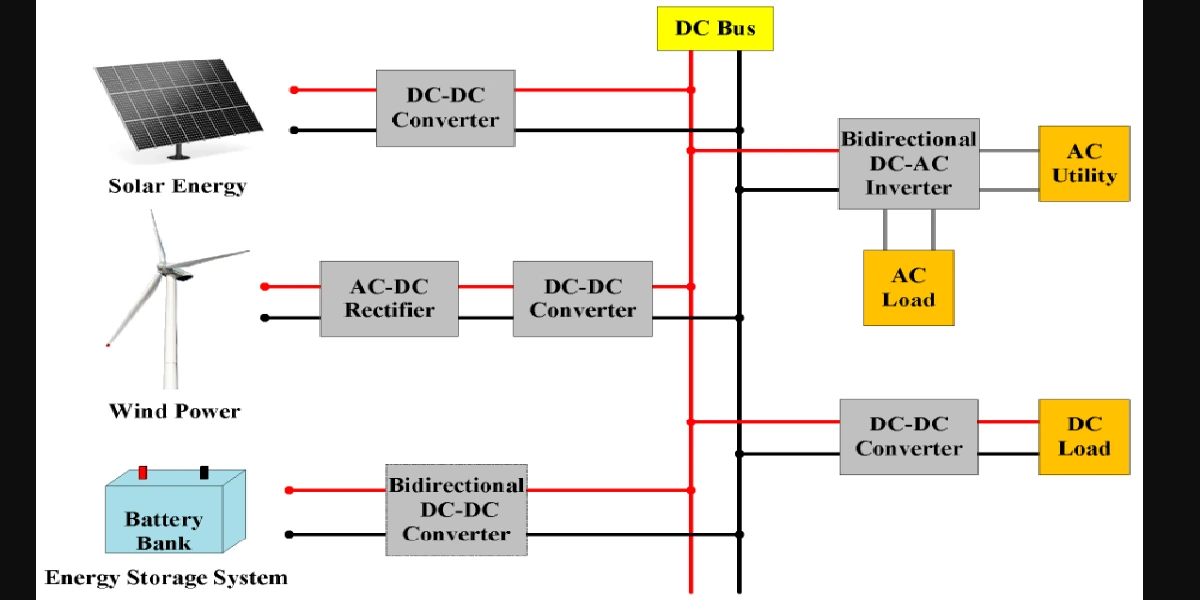
The unit of electric potential is the volt (V), where one volt is one joule per coulomb. One volt is defined as the difference in potential between two points in a conductor which, when carrying a current of one ampere, dissipates a power of one watt, i.e.
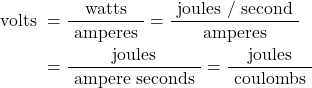
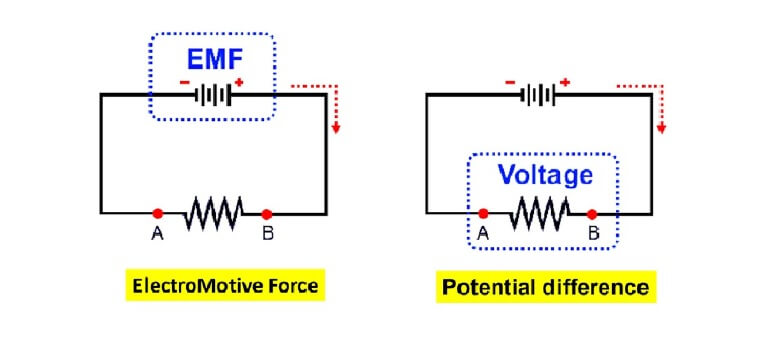
A change in electric potential between two points in an electric circuit is called a potential difference. The electromotive force (e.m.f.) provided by a source of energy such as a battery or a generator is measured in volts.
| Read More Topics |
| Frequency of induced emf in rotor |
| EMF equation of a transformer |
| Duddell’s oscillograph elements |
| Plasma etching and reactive ion etching |