The thermistor is a semiconductor device that has a negative temperature coefficient of resistance. Thermistors are non-metallic resistors, that is, semiconductors of ceramic materials.
Basic Principle :
The basic principle involved in thermistor is, when it is subjected to a temperature change, the resistance of the thermistor changes. This change in resistance will be the increase in temperature.
Construction :
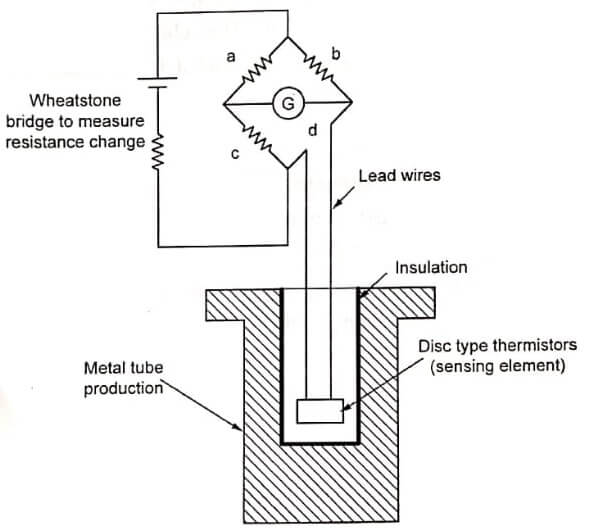
The thermistor has a bridge amplifier circuit which may be employed with resistance thermometer or thermistor devices. A metal tube has a thermistor sensing element. The combination of a metal tube and sensing element leads is used to measure the temperature.
Working :
Initially, a known constant current is passed through the thermistor sensing element and change in resistance is measured.
After taking the initial measurement, the thermistor is introduced into the medium whose temperature is to be measured. Due to the change in temperature, the thermistor sensing element gets heated and the change in resistance will occur. This change in resistance is measured using the wheat stone bridge and it is the measure of the medium temperature.
Applications :
- It is used for varying temperatures.
- It is used in time delay circuits.
- Thermistors are used for temperature compensation.
- It is used to measure pressure and flow of liquids.
- It is used in time delay circuits.
Advantages :
- Very high accuracy.
- It can be manufactured for very small sizes.
- It is used to measure very high temperature.
- It has the ability to withstand mechanical and electrical stresses.
Limitations :
- Self heating may occur.
- Highly non-linear behavior over its range of operation.
- It is possible in thermistor an increase of the resistance when time lapses.
- See More : Electrical comparator working principle
- See More : How do hall sensor working
- See More : Analog link in optical communication
- See More : Control system in mechatronics