Emotional Labour
Definition
Emotional labour is an employee expression of organization desired emotions during interpersonal transaction at work.
According to Morris and Feldman, “Emotional labour is the effort, planning, and control needed to express organizationally desired emotions during interpersonal transactions”.
Forms of Emotional Labour
- Surface Acting- Surface acting involves an employee’s emotions on his ‘surface’ without actually feeling them.
- Deep Acting- Inner feelings.
Emotional Labour in organization and its implication
Service workers typically need to perform in a certain manner if they are going to provide high quality service. The pattern of behaviour is usually defined by the management to them and it is strictly regulated and monitored. The rules speak that customers are always right, and speak to customers with polite words and treat customers with smile, and expect them to work in team and exhibit positive team behaviour are all the elements of emotional labour.
In the process of servicing the people, the organization must also help these emotional labours to raise their morale as the job and limit to their, labour turnover and unusual absenteeism. The organization must have the ability to recognize other people’s emotion in order to control and reduce the burden of emotional labour. Sharing success stories to the employees is another effective way of dealing emotional labour. They should be allowed to learn how others successfully deal with the impact of emotional conflict. Thus, if problem are addressed appropriately service workers will often report to tremendous levels of satisfaction and in turn satisfied employees keep customers satisfied.
Emotional Intelligence
Definition
Emotional intelligence helps us monitor our emotions. Emotional intelligence is concerned with an individual’s emotional and social skills. EI help us monitor and scope our emotional response of others.
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to perceive, control and evaluate emotions. Some researchers suggest that emotional intelligence can be learned and strengthened but some says it is an inborn characteristic.
According to Peter Salovey and John D. Mayer, (1990) “Emotional Intelligence as, the subset of social intelligence that involves the ability to monitor one’s own and others feelings and emotions, to discriminate among them and to use this information to guide ones thinking actions”.
According to Daniel Goleman, “EI is the capacity for recognizing our own feelings and those of others, for motivating our-selves, and for managing emotions well in ourselves and in our relationship”.
EIQ- Emotional Intelligence Quotient describes an ability, capacity, or skill to perceive, assess, and manage the emotions of one’s self, of others, and of groups.
Nature of Emotional Intelligence
a. Identification of Emotion
b. Perception of Emotion
c. Expression of Emotion
d. Understanding of Emotions
e. Management of Emotion
a. Identification of Emotion: The ability to identify emotions is something we develop quite early in life, and our caregivers play an integral role in helping us learn which we are feeling. Emotions are very important to our daily functioning, because they help us guide our decision, help us connect with other people, and keep us out of harm’s way. For example: if we are not able to identify the emotions of “fear” without an ability to recognize fear signals, we might get our self in some pretty dangerous situation.
b. Perception of Emotion: Emotions control our thinking, behaviour and action. It is culture specific. We perceive certain basic emotions like happiness, sadness, fear and anger which is actually hard-wired into our brains from birth. We strongly believe that the way we perceive these emotions isn’t truly affected by our personnel experience. But in terms of facial expression one can easily perceive that they are happy, sad, angry and fearful in the manner they posture, these perceptions are something we are born with and not that we learned.
c. Expression of Emotion
d. Understanding of Emotions
e. Management of Emotion
Importance of Emotional Intelligence
- Improves relationship
- Improves communication with others
- Better empathy skills
- Acting with integrity
- Respect from others
- Improved career prospects
- Manage change more confidently
Theories of Emotional Intelligence- Three Theories
1. Ability Model Theory: It is viewed as a standard intelligence. The model measures emotional intelligence as a mental ability in the performance assessments that have a criterion of correctness. (i.e., this approach use self-report instruments as opposed to performance assessments to measure emotional intelligence) which means instead of asking people to demonstrate how they perceive an emotional expression accurately, self-report measures ask people to judge and report how good they are at perceiving others emotions accurately.
Thus, under this ability model of intelligence, each ability influences how individuals utilize emotions to facilitate thinking or regulate emotions to focus on important information.
The ability to perceive emotion, integrate emotion to facilitate thought, understand emotions, and to regulate emotions to promote economic growth.
2. Mixed Models of EI: Models that mix together emotional intelligence qualities with other personality traits unrelated to either emotion or intelligence are often referred to as mixed models of emotional intelligence. Under this, the model mixes together the core idea of emotional intelligence with a variety of other personality traits, like team work, initiatives, achievement motivation etc…
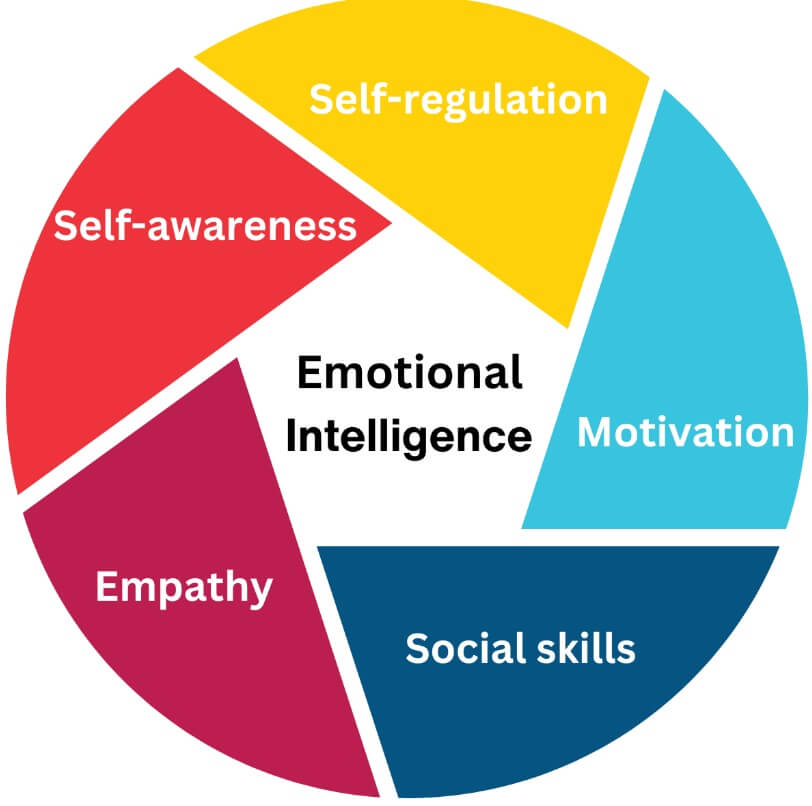
The five factors of mixed models are;
a. Self awareness
b. Self-management
c. Motivation
d. Empathy
e. Social skills
a. Self Awareness: It is about ability to recognize our own emotions and effects. It is about sure on self worthiness and capabilities.
b. Self Management: It is about self control, maintaining standards of honesty. Taking responsibility of our own performance. Handling change with flexibility. Being open to new ideas.
c. Motivation: It is about motivating self for any achievements requires clear goals and a positive attitude. The constant striving to improve standard of excellence, strong commitments, with the goals of the group or organization. Pursuing goals persistently despite obstacles and setbacks.
d. Empathy: It is about recognizing our self on how people feel is important to success in our life and career.
e. Social Skills: It is about developing good interpersonal relationship. Pass clear communication, inspire and guide groups and people. Manage change properly; builds hand will have ability to work with others towards shared goals. Team capabilities, creating group to achieve collective goals.
3. Trait EI Model: It refers to an individual self- perception of their emotional abilities. It is a constellation of emotional perception located at the lower levels of personality hierarchies. Trait emotion, intelligence essentially concerns peoples self perceptions of their emotional abilities. For example on the context of adaptability the high scorers perceives themselves as flexible and willing to adapt to new conditions, on the context of emotion expression, the high scorers perceive themselves as capable of communicating their feelings to others.
| Read More Topics |
| Definition and meaning for impression management |
| Define value and sources of value |
| Define learning and list the theories of learning |