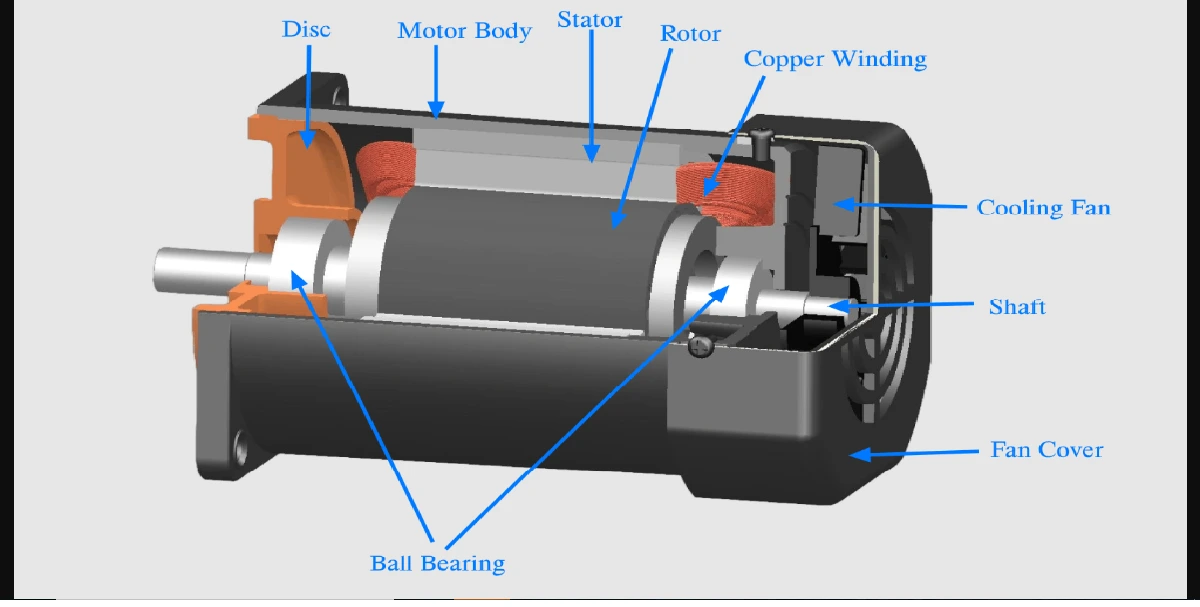
It is a signal phase motor whose operation depends upon the hysteresis (magnetisation produced in a ferromagnetic material lags behind the magnetising force) and on the presence of continuously revolving magnetic flux.
Construction
- A stator designed to produce a synchronously revolving field from a single phase supply. This is accomplished by using permanent split capacitor type construction. Consequently the starting as well as main winding remain connected in the circuit during running operation as well as starting. The value of capacitance is so adjusted as to result in a flux revolving at synchronous speed.
- A rotor consisting of a smooth cylinder of magnetically hard steel, without winding or teeth.
Operation
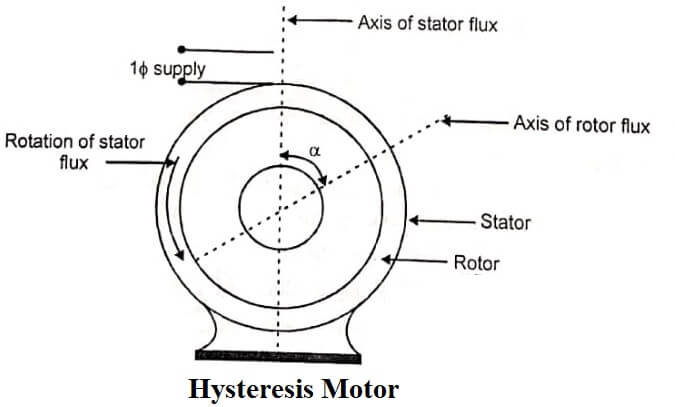
When the stator is energised from a single-phase supply, a synchronously revolving field (assmed in anticlockwise direction) is produced due to split phase operation..
The revolving stator flux magnetises, the rotor. Due to hysteresis effect, the axis of magnetisation of rotor will lag behind the axis of stator field by hysteresis lag angle as shown in figure. If the rotor is stationary the starting torque produced is given by Ts α Φs Φr sin α
where Φs– stator flux, Φr – rotor flux
Now, the rotor accelerates to synchronous speed with a uniform torque.
After reaching synchronism, the motor continues to run at synchronous speed and adjusts its torque angle so as to develop the torque required by the load.
Characteristics
- A hysteresis motor can synchronise any load which it can accelerate, no matter how great the intertia is: it is because the torque is uniform from standstill to synchronous speed.
- Since the rotor has no teeth or salient poles or winding, a hysteresis motor is inherently quiet and produces smooth rotation of the load.
- The rotor takes on the same number of poles as the stator field. Thus by changing the number of stator poles through pole-changing connections, we can get a set of synchronous speeds for the motor.
Applications
Due to their quiet operation and ability to drive high-inertia loads, hysteresis motors are used for driving i) electric clocks ii) timing devices (iii) tape-decks (iv) turn tables and other precision equipment.
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h2″ img=”” question=”What is a hysteresis motor?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] It is a single phase motor whose operation depends upon the hysteresis effect (magnetisation produced in a ferromagnetic material lags behind the magnetising force) and on the presence of continuously revolving magnetic flux. [/sc_fs_faq]
- See More : Torque of synchronous motor
- See More : Repulsion motor types
- See More : Frequency of induced emf