In recombinant DNA (rDNA/rec DNA) technology, DNA molecules from two different sources are joined and inserted into a host organism to get products useful for human use (figure). A clone refers to a group of cells or organisms obtained from one progenitor, thus indicating that the members of a clone are genetically same. This is because each time identical daughter cells are formed by cell replication. The word clone associated with recombinant DNA technology provides the ability to produce several copies of a single DNA fragment, like a gene, creating identical copies producing a DNA clone.
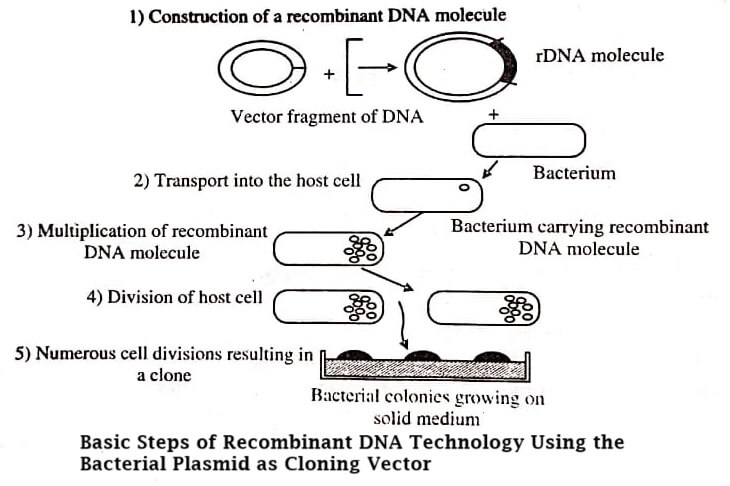
Steps Involved
Strategies for gene cloning along with the techniques commonly employed are mentioned below:
Isolation of target DNA by:
- Restriction endonuclease digestion,
- cDNA clones,
- Mechanical shearing, and
- Chemical synthesis.
Insertion of target DNA into a vector by:
- Direct ligation of cohesive termini,
- Blunt end ligation,
- Linkers and adapters, and
- Homopolymer tailing.
Cloning vectors:
- Plasmids,
- Bacteriophages,
- Cosmids,
- Phagemids,
- Vectors for cloning larger DNA fragments,
- Vectors for preparing single-stranded DNA, and
- Expression vectors.
Identification and isolation of recombinant genes.
Expression of cloned genes within the host.
| Read More Topics |
| Genetic engineering |
| Effect of substituents on acidity |
| Aromatic character/aromaticity |