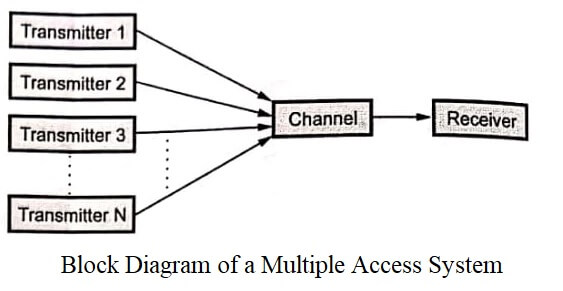
Because of the development in communications and computer fields, the applications involving multiple users are also growing. For example, a cellular telephone network involve large number of mobile subscribers which communicate with each other through their base stations. Other example is satellite networks where transmission between multiple users is through satellites. The multiple users share common transmission channel and repeaters such as satellites.
The successful sharing of those resources and operation is broadly called as multiuser communications. Majority of multiuser communication today use multiple access techniques such as FDMA, TDMA and CDMA. Standard protocols such as CSMA are also used for multiuser communications. The multiuser communications can be implemented with the help of multiple access techniques. The communication channel is shared by large number of users. Fig shows such multiple access system. The common channel can be the uplink of the satellite or the cable of the computer network.
- FDMA – Frequency Division Multiple Access
- TDMA – Time Division Access
- CDMA – Code Division Multiple Access
The broadcast network is also an example of multiuser communication system. The downlink transmission of satellite, radio and TV transmissions are the examples of such systems. The multiple access methods and broadcast networks are widely used multiuser communication systems. The next type of multiuser communication system is store and forward network. This network can be implemented with the help of satellite relay stations.
The relay station receives data and then forwards it to the next relay station or receiver. The two way communication system is also a multiuser system. The two way communication system consists of transmitter and receiver at every end and the common communication channel. Let us consider the multiple access methods of multiuser communication in this section.
Frequency Division Multiple Access
- In this method the channel bandwidth is subdivided into non- overlapping subchannels. This is illustrated in Fig.
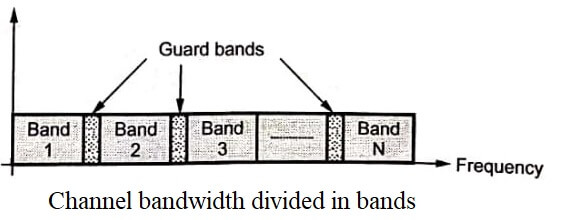
- As shown in above figure there are ‘N’ bands which are non-overlapping.
- Each channel is assigned the frequency slot (band) permanently.
- All the users can transmit their information simultaneously over the band alloted to them.
- The bands are isolated from each other by guard bands. These guard bands are necessary to avoid interchannel interference.
Advantages of FDMA
- The users can transmit continuously without any interruption.
- The channel bandwidth is utilized more efficiently.
- No synchronization or codeword is required in FDMA.
Disadvantages of FDMA
- Extra guard bands are required to avoid interchannel interference.
- There is the possibility of intermodulation distortion at the transponder.
- Power efficiency is reduced.
Applications
- FDMA is used for wireline channels for voice and data transmission.
- Telephone communication.
Time Division Multiple Access
- In this method, each channel is assigned a fixed time slot and complete bandwidth in the frame.
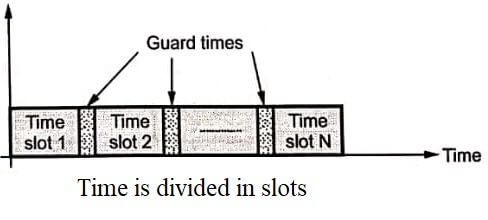
- Each channel transmits in a particular time slot. It uses full bandwidth.
- Normally pulse modulation systems used TDMA. Between the successive pulses of the same channel, other channels can send their data.
- Guard times are necessary between the time slots to avoid interference among the channels.
- The transmission from various users need to be synchronized between transmitter and receiver.
TDMA Frame
Fig shows the basic frame of TDMA.
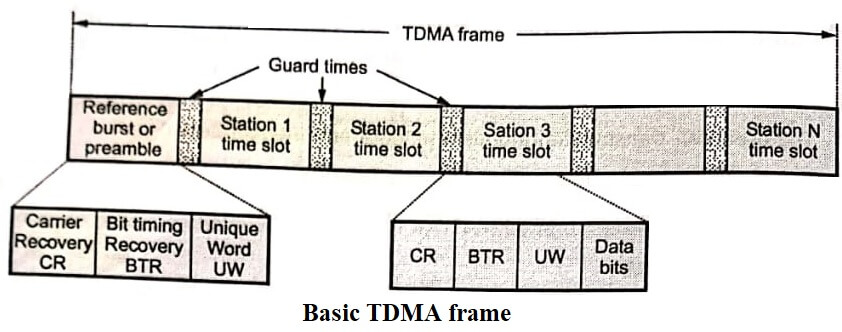
Reference Burst or Preamble
This is used for synchronization. There can be more than one reference bursts. It contains three different sequences.
- Carrier Recovery sequence (CR) : It contains information of frequency and phase of carrier. The earth stations generate local carrier from this sequence.
- Bit Timing Recovery (BTR) : From this sequence earth stations recover the clock.
- Unique word : This sequence is used for timing reference for synchronization of transmission of the reference burst. Unique word is the string of twenty successive 1’s and it is terminated by zero.
Advantages of TDMA
- The user gets full bandwidth of the channel in a particular time slot.
- For bursty signals such as voice or speech TDMA gives maximum utilization of the channel.
- Most suitable technique for digital transmission.
Disadvantages of TDMA
- It is not much suitable for continuous signals.
- Extra guard times are necessary.
- Synchronization is necessary.
Applications
- TDMA is used for voice and data transmission.
- Bursty signals can be transmitted using TDMA.
Code Division Multiple Access
- In this method every user is assigned the unique code sequence or signature sequence. The signal is then spread across the complete frequency band with the help of this code. At the receiver, the signal is recovered with the help of same code.
- Since the signals in CDMA spread over the complete frequency band, it is also called Spread Spectrum Multiple Access (SSMA).
- Access to the user is given randomly. Hence signal transmissions from various overlap in time as well as frequency. Fig illustrates CDMA concept.
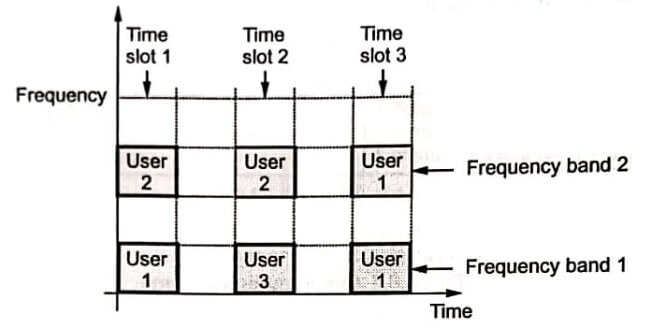
Avoiding interference using CDMA
- The transmission from channels is suppressed in inactive periods. This reduces the interferences and makes the transmission slot available to other channels.
- The in cell interference can be completely avoided through the use of orthogonal spreading codes.
- The reduction of in cell interference also mitigates the need for power control.
- As the number of users are increased in CDMA, the noise floor increases in linear manner.
- Since the signal is spread over a large spectrum, multipath fading is substantially reduced.
- The near-far problem can be avoided in CDMA by adaptive power control of the channels.
Advantages
- Maximum utilization of the channel takes place.
- Synchronization is not necessary.
Disadvantages
- Chance of data collision because of overlap.
- Protocols are necessary to avoid collision.
| Read More Topics |
| Basic communication system |
| Computer control of power system |
| Database management system |