here’s a basic cheat sheet for Oracle SQL
SELECT Query
SELECT col1, col2
FROM table
JOIN table2 ON table1.col = table2.col
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name
HAVING condition
ORDER BY col1 ASC|DESC;
SELECT Keywords
| DISTINCT: Removes duplicate results |
SELECT DISTINCT product_name |
| BETWEEN: Matches a value between two other values (inclusive) |
SELECT product_name |
| IN: Matches to any of the values in a list |
SELECT product_name |
| LIKE: Performs wildcard matches using _ or % |
SELECT product_name |
Joins
SELECT t1.*, t2.*
FROM t1
join_type t2 ON t1.col = t2.col;
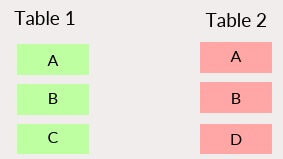
| INNER JOIN: show all matching records in both tables. |
 |
| LEFT JOIN: show all records from left table, and any matching records from right table. | 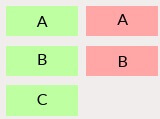 |
| RIGHT JOIN: show all records from right table, and any matching records from left table. |
 |
| FULL JOIN: show all records from both tables, whether there is a match or not. |
 |
CASE Statement
Simple Case
CASE name
WHEN 'John' THEN 'Name John'
WHEN 'Steve' THEN 'Name Steve'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END
Searched Case
CASE
WHEN name='John' THEN 'Name John'
WHEN name='Steve' THEN 'Name Steve'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END
Common Table Expression
WITH queryname AS (
SELECT col1, col2
FROM firsttable)
SELECT col1, col2..
FROM queryname...;
Modifying Data
| Insert | INSERT INTO tablename |
| Insert from a Table |
INSERT INTO tablename |
| Insert Multiple Rows |
INSERT |
| Update | UPDATE tablename |
| Update with a Join |
UPDATE t |
| Delete | DELETE FROM tablename |
Indexes
Create Index
CREATE INDEX indexname
ON tablename (cols);
Drop Index
DROP INDEX indexname;
Set Operators
| UNION: Shows unique rows from two result sets. |
 |
| UNION ALL: Shows all rows from two result sets. |
 |
| INTERSECT: Shows rows that exist in both result sets. |
 |
| EXCEPT: Shows rows that exist in the first result set but not the second. |
 |
Aggregate Functions
SUM: Finds a total of the numbers provided
COUNT: Finds the number of records
AVG: Finds the average of the numbers provided
MIN: Finds the lowest of the numbers provided
MAX: Finds the highest of the numbers provided
Common Functions
- LENGTH(string): Returns the length of the provided string
INSTR(string, substring, [start_position], [occurrence]): Returns the position of the substring within the specified string. - TO_CHAR(input_value, [fmt_mask], [nls_param]): Converts a date
or a number to a string - TO_DATE(charvalue, [fmt_mask], [nls_date_lang]): Converts a
string to a date value. - TO_NUMBER(input_value, [fmt_mask], [nls_param]): Converts a
string value to a number. - ADD_MONTHS(input_date, num_months): Adds a number of
months to a specified date. - SYSDATE: Returns the current date, including time.
- CEIL(input_val): Returns the smallest integer greater than the
provided number. - FLOOR(input_val): Returns the largest integer less than the
provided number. - ROUND(input_val, round_to): Rounds a number to a specified
number of decimal places. - TRUNC(input_value, dec_or_fmt): Truncates a number or date to a
number of decimals or format. - REPLACE(whole_string, string_to_replace, [replacement_string]):
Replaces one string inside the whole string with another string. - SUBSTR(string, start_position, [length]): Returns part of a value,
based on a position and length.
Create Table
| Create Table | CREATE TABLE tablename ( |
Create Table with Constraints
CREATE TABLE tablename (
column_name data_type NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT pkname PRIMARY KEY (col),
CONSTRAINT fkname FOREIGN KEY (col)
REFERENCES other_table(col_in_other_table),
CONSTRAINT ucname UNIQUE (col),
CONSTRAINT ckname CHECK (conditions)
);
| Create Temporary Table |
CREATE GLOBAL TEMPORARY TABLE |
| Drop Table | DROP TABLE tablename; |
Alter Table
| Add Column | ALTER TABLE tablename |
| Drop Column | ALTER TABLE tablename |
| Modify Column | ALTER TABLE tablename MODIFY |
| Rename Column | ALTER TABLE tablename RENAME COLUMN |
| Add Constraint | ALTER TABLE tablename ADD |
| Drop Constraint | ALTER TABLE tablename DROP |
| Rename Table | sp_rename |
Window/Analytic Functions
function_name ( arguments ) OVER (
[query_partition_clause]
[ORDER BY order_by_clause
[windowing_clause] ] )
Example using RANK, showing the student details and their rank according to the fees_paid, grouped by gender:
SELECT
student_id, first_name, last_name, gender, fees_paid,
RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY gender ORDER BY fees_paid
) AS rank_val
FROM student;
Subqueries
| Single Row | SELECT id, last_name, salary |
| Multi Row | SELECT id, last_name, salary |
| Read More Topics |
| HTML cheat sheet with examples |
| OOPs Interview Questions |
| Python interview questions and answers for freshers |