An SQL Server Cheat Sheet is a quick reference guide or document that provides concise and handy information about SQL Server commands, syntax, and commonly used queries. It’s a helpful resource for database administrators, developers, or anyone working with SQL Server databases who wants to quickly look up commands or refresh their memory on how to perform specific tasks. The cheat sheet typically includes essential SQL Server commands for tasks like querying data, updating records, creating tables, and managing database permissions. It’s a great tool for efficiency and accuracy when working with SQL Server databases.
SELECT Query
SELECT col1, col2
FROM table
JOIN table2 ON table1.col = table2.col
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name
HAVING condition
ORDER BY col1 ASC|DESC;
SELECT Keywords
| DISTINCT: Removes duplicate results |
SELECT DISTINCT product_name |
| BETWEEN: Matches a value between two other values (inclusive) |
SELECT product_name |
| IN: Matches to any of the values in a list |
SELECT product_name |
| LIKE: Performs wildcard matches using _ or % |
SELECT product_name |
Joins
SELECT t1.*, t2.*
FROM t1
join_type t2 ON t1.col = t2.col;
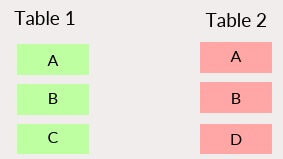
| INNER JOIN: show all matching records in both tables. |
 |
| LEFT JOIN: show all records from left table, and any matching records from right table. | 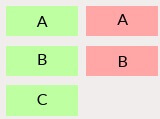 |
| RIGHT JOIN: show all records from right table, and any matching records from left table. |
 |
| FULL JOIN: show all records from both tables, whether there is a match or not. |
 |
CASE Statement
Simple Case
CASE name
WHEN 'John' THEN 'Name John'
WHEN 'Steve' THEN 'Name Steve'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END
Searched Case
CASE
WHEN name='John' THEN 'Name John'
WHEN name='Steve' THEN 'Name Steve'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END
Common Table Expression
WITH queryname (col1, col2...) AS (
SELECT col1, col2
FROM firsttable)
SELECT col1, col2..
FROM queryname...;
Modifying Data
| Insert | INSERT INTO tablename |
| Insert from a Table |
INSERT INTO tablename(col1, col2...)SELECT col1, col2... |
| Insert Multiple Rows |
INSERT INTO tablename(col1, col2...) VALUES(valA1, valB1),(valA2, valB2),(valA3, valB3); |
| Update | UPDATE tablename |
| Update with a Join |
UPDATE t |
| Delete | DELETE FROM tablename |
Indexes
| Create Index | CREATE INDEX indexname |
| Drop Index | DROP INDEX indexname; |
Set Operators
| UNION: Shows unique rows from two result sets. |
 |
| UNION ALL: Shows all rows from two result sets. |
 |
| INTERSECT: Shows rows that exist in both result sets. |
 |
| MINUS: Shows rows that exist in the first result set but not the second. |
 |
Aggregate Functions
SUM: Finds a total of the numbers provided
COUNT: Finds the number of records
AVG: Finds the average of the numbers provided
MIN: Finds the lowest of the numbers provided
MAX: Finds the highest of the numbers provided
Common Functions
- LEN(string): Returns the length of the provided string
- CHARINDEX(string, substring, [start_position], [occurrence]):
Returns the position of the substring within the specified string. - CAST(expression AS type [(length)]): Converts an expression to
another data type. - GETDATE: Returns the current date, including time.
- CEILING(input_val): Returns the smallest integer greater than the
provided number. - FLOOR(input_val): Returns the largest integer less than the
provided number. - ROUND(input_val, round_to, operation): Rounds a number to a
specified number of decimal places. - REPLACE(whole_string, string_to_replace, replacement_string):
Replaces one string inside the whole string with another string. - SUBSTRING(string, start_position, [length]): Returns part of a
value, based on a position and length.
Create Table
| Create Table | CREATE TABLE tablename ( |
Create Table with Constraints
CREATE TABLE tablename (
column_name data_type NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT pkname PRIMARY KEY (col),
CONSTRAINT fkname FOREIGN KEY (col)
REFERENCES other_table(col_in_other_table),
CONSTRAINT ucname UNIQUE (col),
CONSTRAINT ckname CHECK (conditions)
);
| Create Temporary Table |
SELECT cols |
| Drop Table | DROP TABLE tablename; |
Alter Table
| Add Column | ALTER TABLE tablename |
| Drop Column | ALTER TABLE tablename |
| Modify Column | ALTER TABLE tablename ALTER COLUMN columnname newdatatype; |
| Rename Column | sp_rename |
| Add Constraint | ALTER TABLE tablename ADD |
| Drop Constraint | ALTER TABLE tablename |
| Rename Table | ALTER TABLE tablename |
Window/Analytic Functions
function_name ( arguments ) OVER (
[query_partition_clause]
[ORDER BY order_by_clause
[windowing_clause] ] )
Example using RANK, showing the student details and their rank according to the fees_paid, grouped by gender:
SELECT
student_id, first_name, last_name, gender, fees_paid,
RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY gender ORDER BY fees_paid
) AS rank_val
FROM student;
Subqueries
| Single Row | SELECT id, last_name, salary |
| Multi Row | SELECT id, last_name, salary |
| Read More Topics |
| Oracle SQL cheat sheet |
| HTML cheat sheet with examples |
| Object oriented programming interview questions |