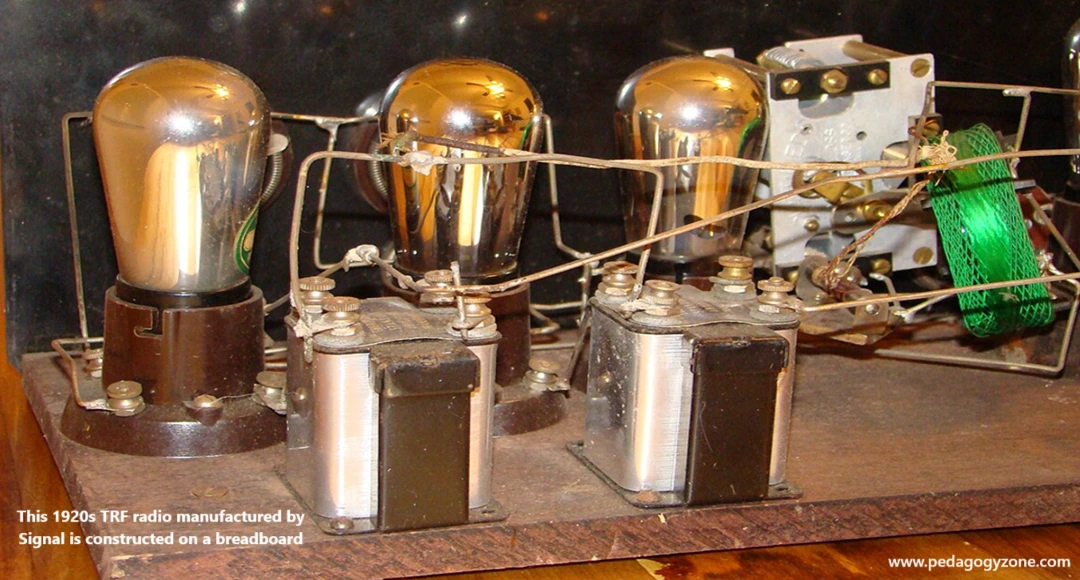
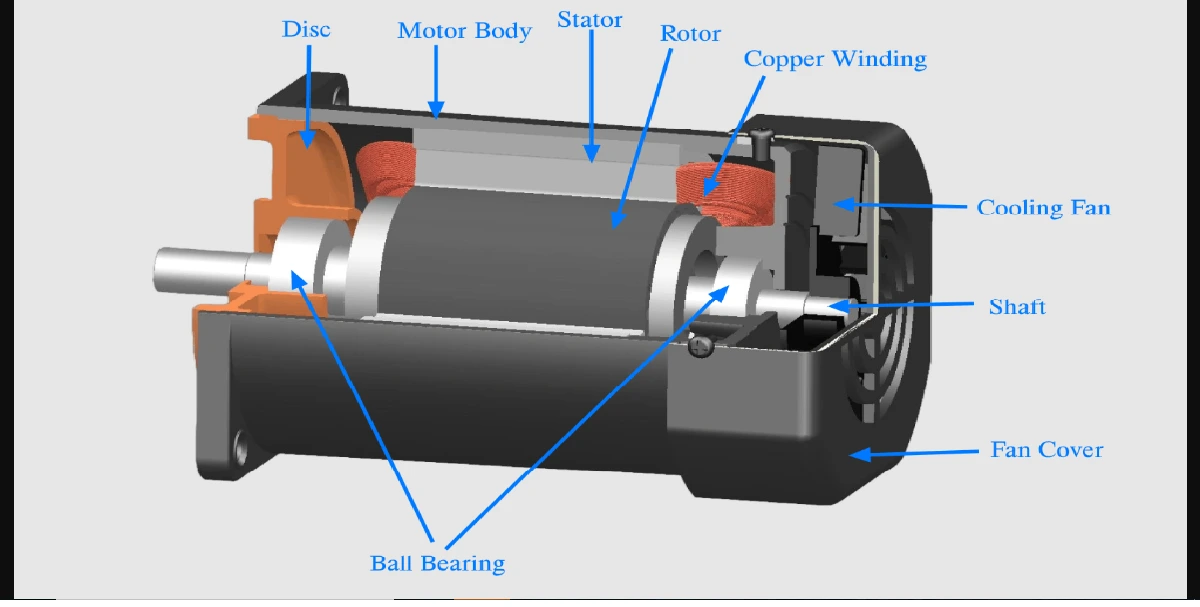
Fig shows the block diagram of Tuned Radio Frequency TRF receiver.
The received signal is weak and noisy. It is given to broadband RF amplifier. The RF amplifier enhances signal to noise ratio and amplifies the signal. It is then passed through AM detector.
The output of AM detector is audio signal. The detected audio signal is then amplified by audio power amplifier. The speaker finally produces the sound.
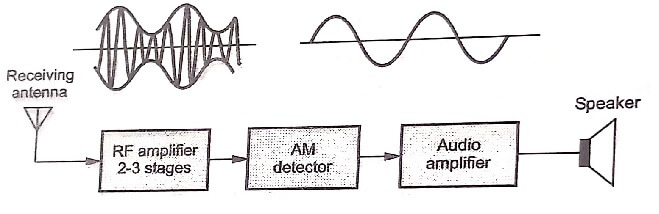
The RF amplifier is tuned to specific frequency which is to be received. Hence if other frequency is to received, then another TRF receiver should be used.
This problem can be solved by using the RF amplifier tuned to wide range of frequencies. But this reduces selectivity of the receiver.
Advantages and Disadvantages of TRF Receiver
Advantages
- Most simplest type of receiver since it does not involve mixing and IF operation.
- Very much suitable to receive single frequency.
- TRF receivers have good sensitivity.
Disadvantages
- Bandwidth changes with center frequency, when TRF receiver is used to receive wide range of frequencies.
- Multiple stages of RF amplifiers are used. This can lead to instability since they all are tuned to same center frequency. Hence stagger tunning is to be used.
- The gain of the TRF receiver is not uniform over wide range of frequencies.
Due to above disadvantages, Tuned Radio Frequency TRF receivers are not practically used in AM receiption. Superheterodyne receivers are commonly used since they offer many advantages.
| Read More Topics |
| Radio over fiber links |
| Transformer rating in kVA |
| Radiographic inspection advantages |