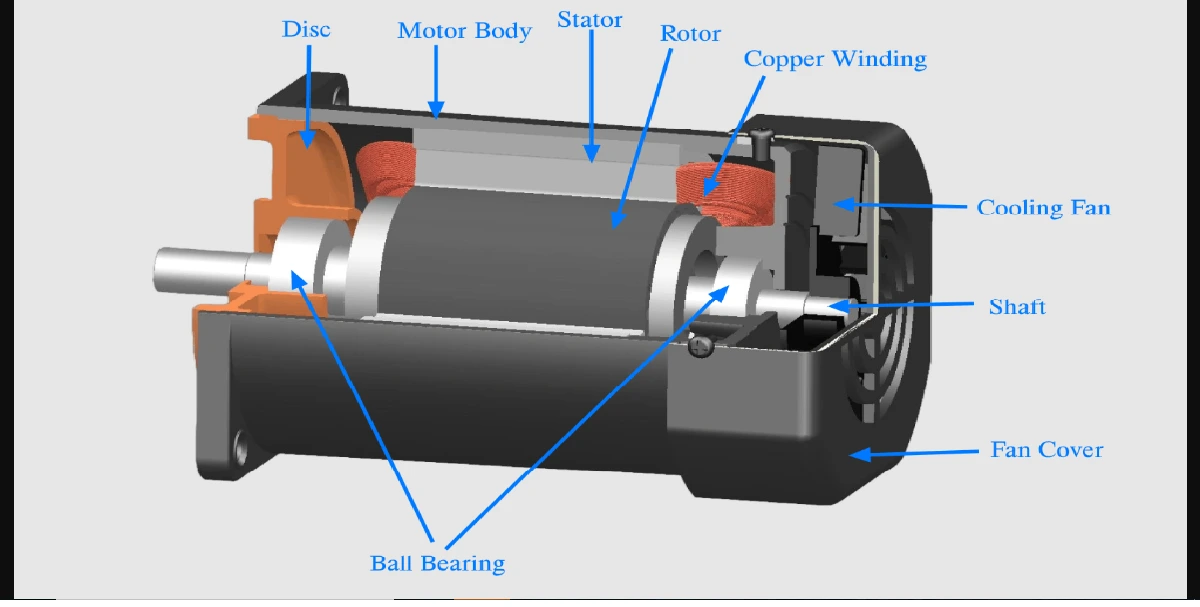
A universal motor is a specially designed series wound motor, that operates at approximately the same speed and output on either dc or ac of approximately same voltage.
Construction
A universal motor is similar to a de series motor in construction. It is constructed with few series field turns, laminated armature and field circuits, low reluctance magnetic path, increased armature conductors and commutator segments and using low flux densities. This is done to minimize the adverse effects caused by high field reactance, eddy currents and hysteresis losses.
The commutation on ac is much poorer than on dc, owing to current induced in the short circuited armature coils, and this provides a definite lamination on their size and utitlity.
If wide brushes are used, the short circuit currents are excessive, and the motor starting torque is reduced; while if narrow brushes are used, there may be excessive brush chatter at high speeds causing short brush life.
Good design therefore needs careful proportioning of commutator and brush rigging to meet conflicting electrical, mechanical and thermal requirements. Brushes employed are high resistance carbon ones so as to aid commutation.
Universal motor may be either compensated (distributed field) or uncompensated (concentrated field) type.
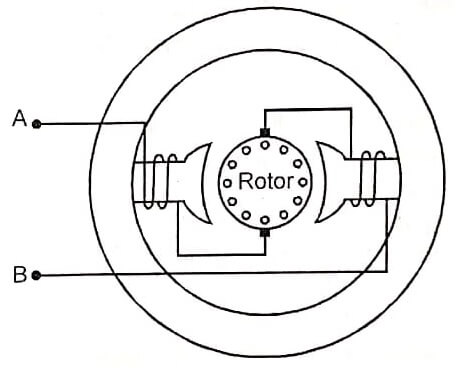
Operation
In a series wound motor the same current flows through field windings and armature, being connected in series with each other, when motor is connected to either dc or ac supply.
The magnetic fields developed by the series field winding and armature currents react with each other and hence develop unidirectional torque.
Applications
- Sewing machines
- High speed vacuum cleaners
- Electric typewriters
- Electric shavers
- Motion picture projectors
- Portable hand tools
- Hair dryers
- Cameras
- Food mixers
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h2″ img=”” question=”What is a universal motor?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] A universal motor is a specially designed series wound motor, that operates at approximately the same speed and output on either dc or ac approximately same voltage. [/sc_fs_faq]
| Read More Topics |
| Single phase induction motor |
| Frequency of induced emf |
| Alternator construction and working |