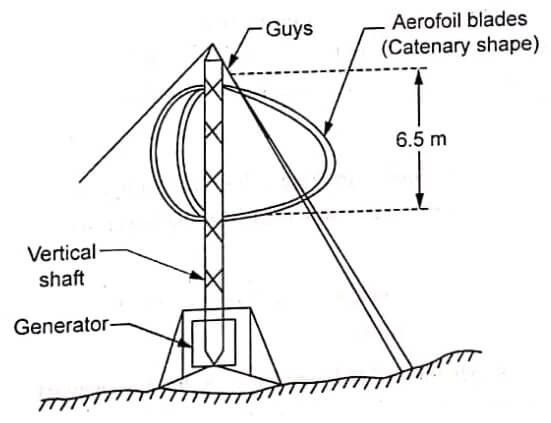
Image shows vertical axis wind turbine type wind machine. One of the main advantages of vertical axis rotors is that they do not have to be turned into the wind steams as the wind direction changes. Because their operation is independent of wind direction, vertical axis machines are called panemones.
Vertical axis wind turbine (or VAWTs) have the main rotor shaft arranged vertically. Key advantages of this arrangement are that the turbine does not need to be pointed into the wind to be effective. This is an advantage on sites where the wind direction is highly variable.
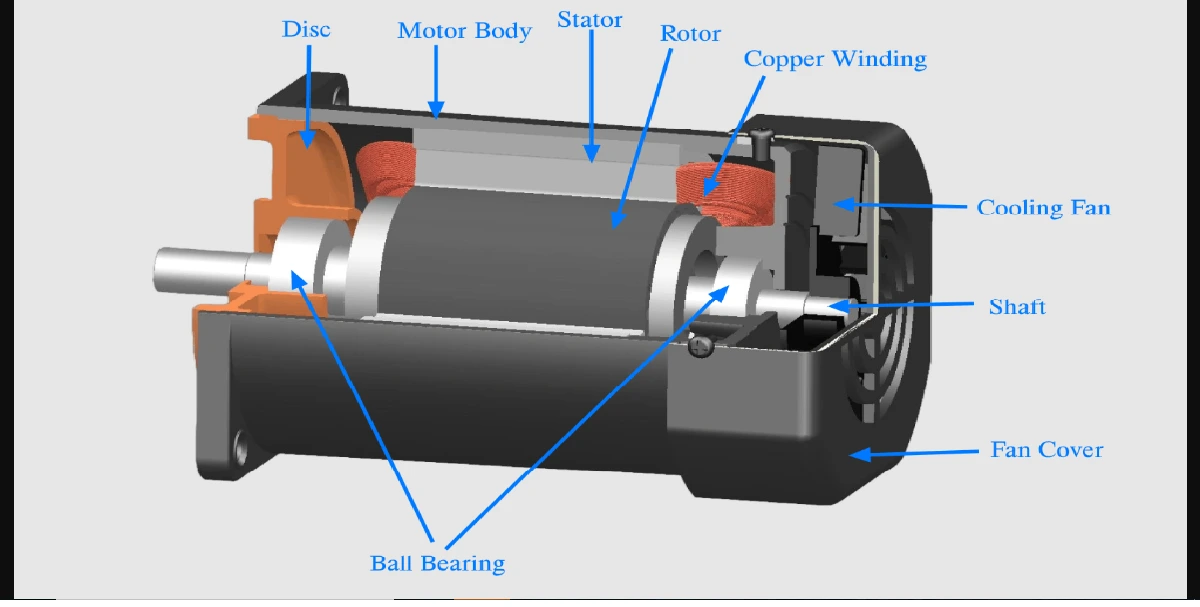
With a vertical axis, the generator and gearbox can be placed near the ground, so the tower does not need to support it, and it is more accessible for maintenance. Drawbacks are that some designs produce
pulsating torque.
It is difficult to mount vertical axis wind turbine on towers, meaning they are often installed nearer to the base on which they rest, such as the ground or a building rooftop. The wind speed is slower at a lower altitude, so less wind energy is available for a given size turbine. Air flow near the ground and other objects can create turbulent flow which can introduce issues of vibration, including noise and bearing wear which may increase the maintenance or shorten the service life. However, when a turbine is mounted on a rooftop, the building generally redirects wind over the roof and this can double the wind speed at the turbine. If the height of the rooftop mounted turbine tower is approximately 50% of the building height, this is near the optimum for maximum wind energy and minimum wind turbulence.
Advantages:
- A massive tower structure is less frequently used, as VAWTs are more frequently mounted with the lower bearing mounted near the ground.
- Designs without yaw mechanisms are possible with fixed pitch rotor designs.
- The generator of a VAWT can be located nearer the ground, making it easier to maintain the moving parts.
- VAWTs have lower wind startup speeds than HAWTS. Typically, they start creating electricity at 6 m.p.h. (10 km/h).
- VAWTs may be built at locations where taller structures are prohibited.
- VAWTs situated close to the ground can take advantage of locations where mesas, hilltops, ridgelines, and passes funnel the wind and increase wind velocity.
- VAWTs may have a lower noise signature.
Disadvantages:
- A VAWT that uses guy wires to hold it in place puts stress on the bottom bearing as all the weight of the rotor is on the bearing.
- The stress in each blade due to wind loading changes sign twice during each revolution as the apparent wind direction moves through 360 degrees.
- While VAWTs’ parts are located on the ground, they are also located under the weight of the structure above it, which can make changing out parts nearly impossible without dismantling the structure if not designed properly.
- Having rotors located close to the ground where wind speeds are lower due to wind shear, VAWTs may not produce as much energy at a given site as a HAWT with the same footprint or height.
| Read More Topics |
| Horizontal axis wind turbine |
| Types of gas turbine power plant |
| Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion |
| Combined cycle nuclear power |