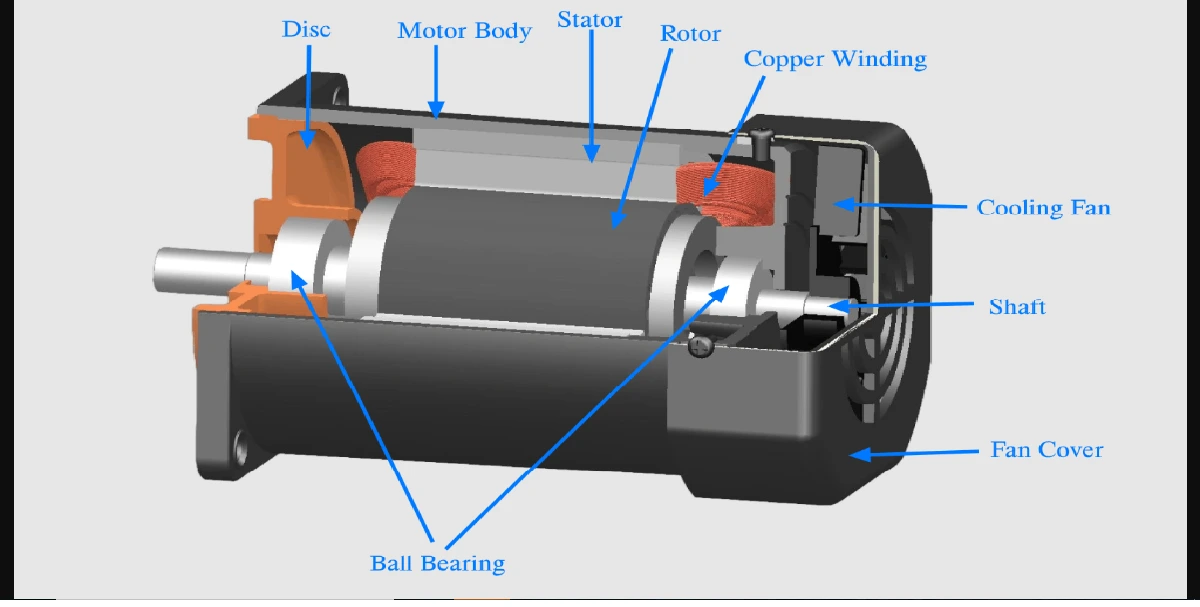
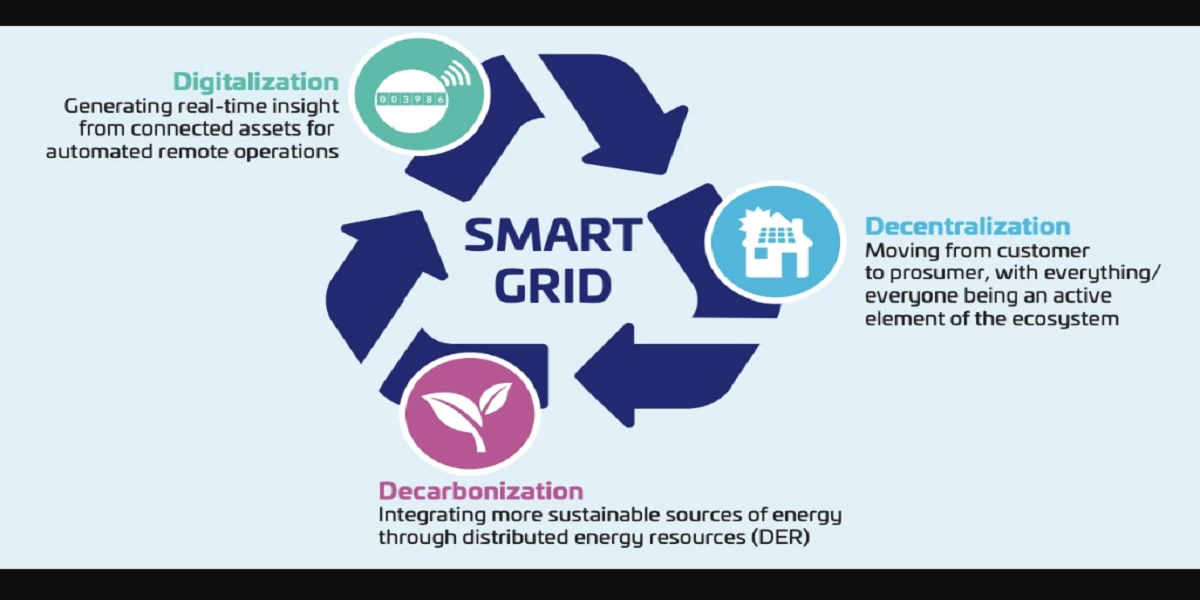
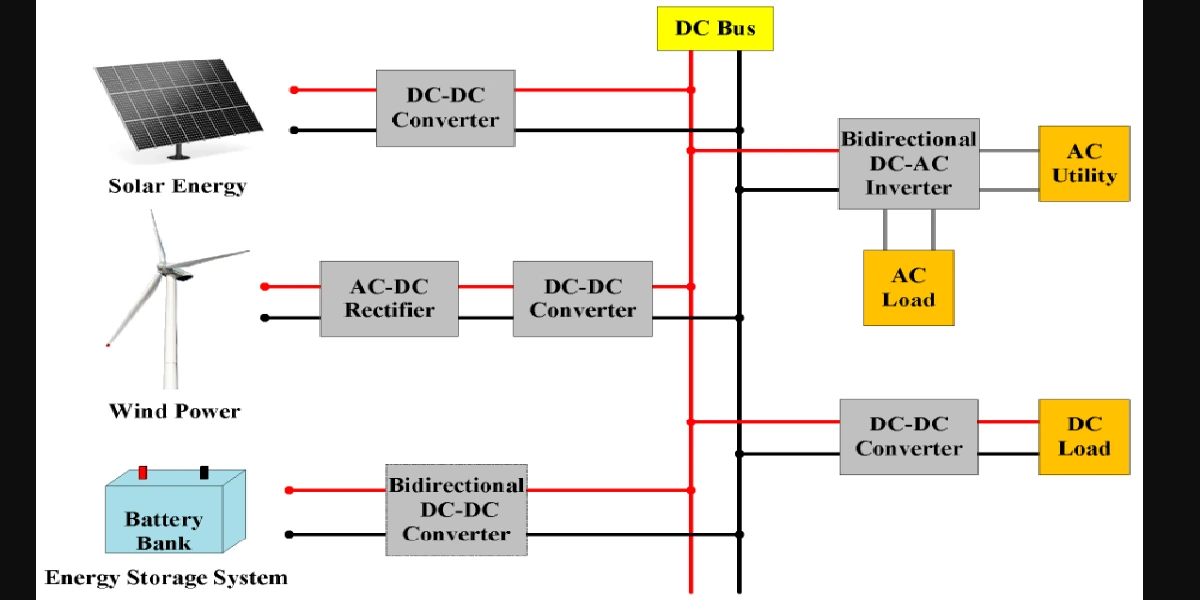
Embedded systems are specialized computing systems designed to perform specific tasks within larger systems. These systems are found in various industries, each tailored to meet specific requirements. The types of embedded systems include real-time embedded systems, networked embedded systems, mobile embedded systems, standalone embedded systems, and more.
Real-time embedded systems are crucial in applications that demand instantaneous responses to stimuli. Networked embedded systems allow devices to communicate and share data over networks. Mobile embedded systems, as the name suggests, are integrated into portable devices like smartphones and wearables. Standalone embedded systems function independently without the need for external resources. Overall, the diverse types of embedded systems cater to a wide range of functions across different domains.
Real-Time Embedded Systems
Real-time embedded systems are designed to respond to events within a strict time frame, ensuring timely and accurate processing of data. These systems are crucial in applications where timing is critical, such as in medical devices, aerospace systems, and industrial control systems. The real-time aspect of these embedded systems is achieved through efficient scheduling algorithms and prioritization of tasks.
In real-time embedded systems, tasks are typically classified as either hard real-time, where missing a deadline can have catastrophic consequences, or soft real-time, where occasional missed deadlines are tolerable. Timing analysis is essential in ensuring that all tasks meet their deadlines, and proper resource management is key to maintaining the system’s performance. By carefully managing the system’s resources and prioritizing tasks based on their importance and timing constraints, real-time embedded systems can effectively operate in time-critical environments.
Networked Embedded Systems
Networked Embedded Systems enable devices to communicate and share information seamlessly over networks. These systems play a crucial role in IoT applications, allowing various devices to connect and exchange data in real-time. By integrating these systems into smart homes, businesses can enhance automation and monitoring capabilities, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
The utilization of Networked Embedded Systems also extends to sectors such as healthcare and transportation, where interconnected devices help streamline operations and improve service delivery. With the evolution of networking technologies like 5G, the potential for these systems to revolutionize industries by enabling faster and more reliable connectivity continues to grow.
Mobile Embedded Systems
Mobile embedded systems are intricately woven into the fabric of our daily lives, powering a wide array of portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology. These systems are designed to be compact, energy-efficient, and highly responsive, allowing users to access a myriad of applications and services seamlessly on the go. With the rapid advancements in hardware and software technologies, mobile embedded systems continuously push the boundaries of innovation, enabling enhanced connectivity and functionality in our handheld devices.
In the realm of mobile embedded systems, one of the key challenges lies in achieving a delicate balance between performance and power efficiency. Engineers strive to optimize system design to deliver high-speed processing capabilities while minimizing energy consumption to prolong battery life. Additionally, the integration of advanced sensors, wireless communication modules, and sophisticated algorithms plays a crucial role in enhancing the user experience and expanding the capabilities of mobile devices. By harnessing the power of mobile embedded systems, developers can create innovative solutions that cater to the evolving needs of modern consumers in an increasingly connected world.
Standalone Embedded Systems
Standalone embedded systems operate independently without the need for a continuous connection to a central network or external devices. These systems are self-contained and are designed to function autonomously, carrying out specific tasks or operations. They are commonly used in scenarios where reliability and robustness are crucial, such as in medical devices, industrial control systems, or appliances.
The programming of standalone embedded systems is typically focused on efficiency and low power consumption to maximize performance while minimizing energy usage. These systems are often designed with specific hardware configurations tailored to their intended functions, ensuring optimized performance for their dedicated tasks. Through careful design and implementation, standalone embedded systems can provide seamless and reliable operation in various applications across different industries.
Embedded Systems in Automotive Applications
Embedded systems play a crucial role in automotive applications, enhancing the performance and functionality of modern vehicles. With the advancement of technology, these systems are becoming more sophisticated and integrated into various components of automobiles. From engine control units to advanced driver assistance systems, embedded systems in automotive applications help ensure efficient operation and improved safety on the roads.
Moreover, the evolution of embedded systems in automotive applications has also led to the development of connected vehicles. These systems enable features such as GPS navigation, real-time traffic updates, and remote vehicle monitoring. By integrating these advanced technologies, automotive manufacturers are able to provide customers with a more seamless driving experience and access to a wide range of smart features while on the go.
Embedded Systems in Consumer Electronics
Embedded systems play a vital role in enhancing the functionalities of consumer electronics. These systems are integrated into devices such as smartphones, smart TVs, cameras, and gaming consoles. They are designed to provide efficient and reliable performance while offering a seamless user experience. The use of embedded systems allows these consumer electronics to perform complex tasks, process data quickly, and communicate with other devices effortlessly.
In consumer electronics, embedded systems are responsible for managing various functions like processing audio and video signals, controlling user interfaces, and enabling connectivity features. One of the key advantages of embedded systems in consumer electronics is their ability to optimize power consumption, ensuring longer battery life for portable devices. Additionally, these systems enable devices to run multiple applications simultaneously, delivering a smooth and responsive user experience.
Embedded Systems in Industrial Automation
Industrial automation heavily relies on embedded systems to control and monitor various processes and machinery. These embedded systems are tailored to meet the specific requirements of industrial applications, ensuring efficient and reliable operation. They play a crucial role in improving productivity, reducing downtime, and enhancing overall operational efficiency in manufacturing plants and industrial facilities.
The integration of embedded systems in industrial automation allows for seamless communication between different components of a system, enabling real-time monitoring and control. With features such as sensor integration, data processing capabilities, and communication interfaces, embedded systems facilitate precision control and automation of processes in industries. Their robust design and ability to withstand harsh industrial environments make them an indispensable part of modern industrial automation systems.
| Read More Topics |
| Primary standard of luminous intensity |
| Microcontroller – Introduction, advantages, features |
| Types of solar collectors for heat |