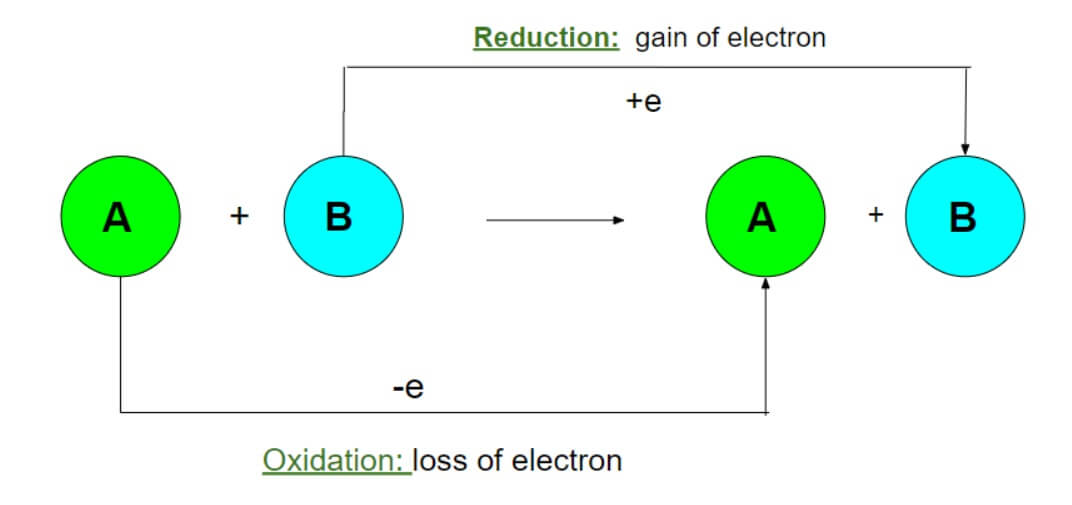
The chemical reactions in which both oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously are called redox reaction.
Oxidation is the process where electrons are lost from a species and reduction is the process where electrons are gained by a species.
On the other hand, the species which reduces other species and itself undergoes oxidation by donating electrons is called reducing agent and the species which oxidises other species and itself undergoes reduction by accepting electrons is called oxidising agent.
Example: If we immerse a Zn rod in an aqueous solution of CuSO4, then after certain time, a reddish brown coloured solid gets deposited on Zn rod and the blue colour (characteristic of the Cu2+ ion) almost disappears (or fades). Reddish-brown coloured solid over Zn rod is simply due to deposition of finely divided Cu metal.
Overall reaction of this process is:
Zn(s) + Cu2 (aq) → Zn2 (aq) + Cu(s).
The oxidation state of Zn increases from 0 to +2 and the oxidation state of Cu decreases from +2 to 0.
Here, Zn acts as a reducing agent or reductant because it donates electrons and consequently reduces the other substance (Cu).
On the other hand, Cu acts as an oxidising agent or oxidant because it accepts electrons and oxidizes Zn.
| Read More Topics |
| How do sodium potassium pumps work? |
| Types of softening of water processes |
| Requirement of boiler feed water |