The electron microscope was first built by Ernest Rush in 1931. It is the type of microscope in which instead of light beam, a beam of electrons are used to form a large image of a very small object. These microscopes are widely used in the field of medicine.
Principle
A stream of electrons is passed through an object and an electrons which carry the information about the object is focused by electric and magnetic fields.
Since, the resolving power is inversely proportional to the wavelength, the electron microscope has high resolving power because of its shorter wavelength (105 times shorter than the wavelength of the visible light).
Construction
An electron microscope is similar to that of an optical microscope. Here, the focusing of electrons can be done either by magnetic lens (or) electrostatic lens. Normally in electron microscope magnetic lenses are used for focusing.
-
Condensing lens to condense the electron of the specimen
-
Objective lens to resolve the structure of the specimen
-
Projector lens, similar to eye piece for enlargement.
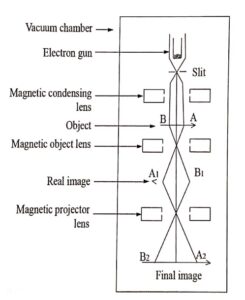
Fig. (1.1) Essential parts of an electron microscope
Working
- Stream of electrons are produced and accelerated by the electron gun.
- The electron beam is made to pass through the centre of the doughnut shaped magnetic condensing lens.
- These electrons are made parallel beam and is focused onto the object AB (Fig.1.1).
- The electrons are transmitted more in the less denser region of the object and as transmitted less by the denser region of the object due to absorption.
- Thus, the transmitted electron beam on falling over the magnetic objective lens, resolves the structure of the object to form a magnified real image of the object.
- Further the image can be magnified by the magnetic projector lens and the final image is obtained on a fluorescent screen.
- In order to make a permanent record of the image of the object, the final image can also be recorded on a photographic plate.
Advantages
-
It can produce magnification as high as 1,00,000 times as that of the size of the object.
-
The focal length of the microscope system can be varied.
Applications
-
It has a very wide area of application in biology, metallurgy, physics, chemistry, medicine, engineering, etc.
-
It is used to determine the complicated structure of the crystals.
-
It is used in the study of colloids.
-
In industries it is used to study the structure of textile fibers, surface of metals, composition of paper, paints etc.
-
In the medical field it is used to study about the structure of virus, bacteria, etc., which are of smaller size.
| Read More Topics |
| Transmission electron microscope principle and working |
| Linear flow of heat along a bar |
| Physical Significance of the Wave Function (ψ) |






