In transmission electron microscope (TEM) the image can be obtained by transmitting the electron through the specimen. TEM is capable of providing information at magnification of 50 million times than that of the object size. This microscope can be used to view the internal features of an atom, morphology of sample of size upto 0.2 mm.
Principle
When the electron beam pass through the specimen, the magnified image is formed on the fluorescent screen, either by transmitted beam (Bright spot) or by diffracted beam (Dark spot).
Construction:
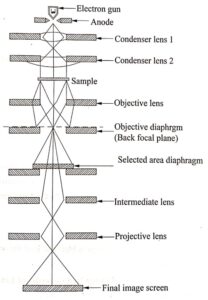
It consists of an electron gun to produce high energy electron. Magnetic condensing lens is used to condense the electron beam. It is also used to adjust the size of the electron beam spot which strike the specimen. The specimen is placed in between the condensing lens and objective lens as shown in the figure (1).
The magnetic objective lens is used to block the high angle diffracted beams and the aperture is used to eliminate the diffracted beam. It also increases the contrast of the image.
The magnetic projector lens is placed above the fluorescent screen helps to obtain higher magnification. The image can be recorded by using fluorescent (phosphor) screen or Charged Coupled Devices (CCD).
The essential components of Transmission Electron Microscope are
Working
- An electron beam emitted from the electron gun is made to pass through the centre of the doughnut shaped electromagnet called condenser lens.
- The electrons get deflected to form parallel beams will strike on the object to be magnified.
- It should be noted that the electrons will be transmitted more through the transparent part of the object and transmitted in less number through comparatively denser portions.
- The transmitted beam will thus have the likeness of the object transversed by it. The second electromagnet called objective lens causes the electron beam to diverge to produce enlarged image of the object.
- The third electromagnet called projector lens focuses the electron beam from part of the enlarged image on the florescent screen producing still greater magnification.
- The image obtained on the fluorescent screen is made visible by scintillation for direct view.
- It can also be obtained on a suitable photographic plate for a permanent record. Sharp focusing is obtained by adjusting the intensity of the magnetic fields produced by electromagnets.
Advantages
-
The resolution of the image is high and is of the order of 1Å to 2 Å.
-
The magnification of image is of the order of 1,000,000 times greater than the size of the object.
-
It can be used to examine specimen size up to 0.2 nm.
-
The focal length of the lens can be controlled by changing the current through the electromagnet.
-
High contrast image can be obtained by both transmitted and diffracted beams.
Limitations
-
It is a time consuming process.
-
Sample must be very thin and not suitable for thicker samples.
-
During sample preparation the structure of the sample may be changed.
-
Three dimensional image cannot be obtained.
-
In biological samples the electron may interact with the samples which cause damage to the sample.
Application
-
The main application of TEM is in nano science. It helps to study the internal features of nano materials.
-
It is used in thin film technology, metallurgy, bio chemistry and microbiology etc.
-
In biological science it is used to study the tomography, reconstruction of cells, virus and bacteria etc.
-
Used to study the composition of paints, paper, fibres and composite materials.
| Read More Topics |
| Electron microscope of principle and working |
| G.P Thomson experiment |
| Physical Significance of the Wave Function (ψ) |





