Introduction
Fuel is a combustible material, which on burning produces larger amount of heat energy.
Fuel + Oxygen → Products + Heat
C + O2 → CO2 + 94°k cal
Heat energy is the main source of power. The reactions are exothermic in nature. During the process of combustion of coal, atoms like carbon and hydrogen combine with oxygen and liberate heat energy. The energy release is due to the rearrangement of valance electrons in these atoms.
The primary source of fuel is coal and petroleum oils, the amounts of which are dwindling day-by-day. These are stored as fuels available in earth’s crust and are generally called as “fossil fuels”.
Definition of fuel
Fuel is a combustible material, which on burning produces larger amount of heat energy.
(or)
A fuel is defined as any combustible substance which is obtainable in bulk and which when burnt in atmospheric air in such a manner, the heat evolved is capable of being economically used for domestic and industrial purposes for heating and generation of power.
Characteristics or requirement of a good fuel
The following are the characteristics of good fuels:
- They should be readily available and in large quantities.
- Their storage and transportation should be safe and easy.
- They should have moderate rate of combustion.
- They should not leave much ash behind.
- They should not pollute the air on burning.
- They should have optimum ignition temperature.
- They should have high calorific value.
Classification of Fuels
Fuels obtained directly from the nature are called as natural or primary fuels and Fuels which are derived from the natural or primary fuels are called as derived or secondary fuels.
Difference between primary and secondary fuels
| Primary fuels | Secondary fuels |
| They occur in nature. | They are derived from primary fuels. |
| They are also called as natural fuels. | They are also called as processed fuels. |
| Eg : Wood, coal, petroleum and natural gas. | Eg : Coke, charcoal, kerosene oil, diesel oil, water gas and coal gas etc. |
Depending on their physical states, fuels are classified as
- solid fuels,
- liquid fuels and
- gaseous fuels.
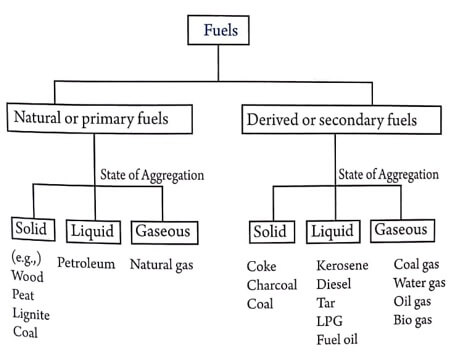
Comparative statement of solid, liquid and gaseous fuels.
| Solid fuels | Liquid fuels | Gaseous fuels |
| Cheap and easily available. | More costly than solid fuels. | Gaseous fuels are costlier (except natural gas). |
| Less risk of fire hazard. | Greater risk of fire hazard. | Chances of fire hazards are more. |
| Storage and transportation are comparatively easier. | Care must be taken if liquid fuels are taken in closed containers. | Storage and transportation are difficult and proper care is neede. |
| Slow combustion takes place. | Quick combustion takes place. | Combustion takes place rapidly and efficiently. |
| They burn in large excess of air. | They burn in slight excess of air | They also burn in slight excess of air |
| W/W calorific value is least. | W/W calorific value is Higher. | W/W calorific value is highest. |
| Ash is produced and its disposal is a problem. | Ash is not produced and burning is clean. | Ash and smoke are not produced. |
| Thermal efficiency is least. | Thermal efficiency is higher than solid fuels. | Thermal efficiency is highest. |
| Can not be used in internal combustion engines. | Can be used in internal combustion engines. | Can be used in internal combustion engines. |
| Read More Topics |
| Explain briefly the manufacture of glass |
| Give a brief account of different kinds of glass |
| Constituents of glass and their functions |





