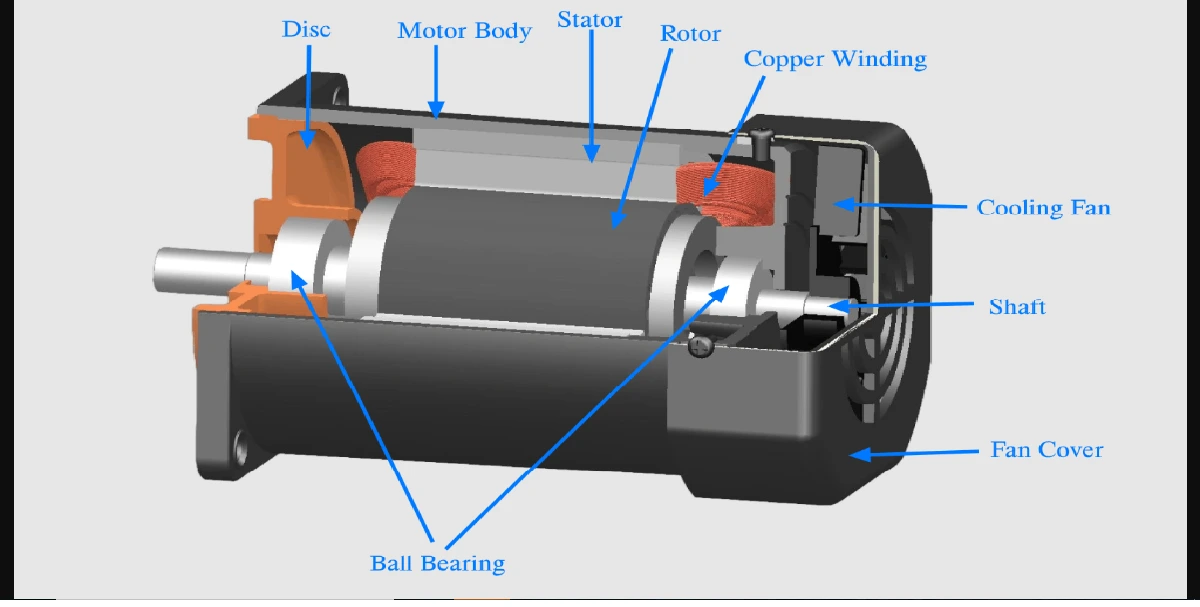
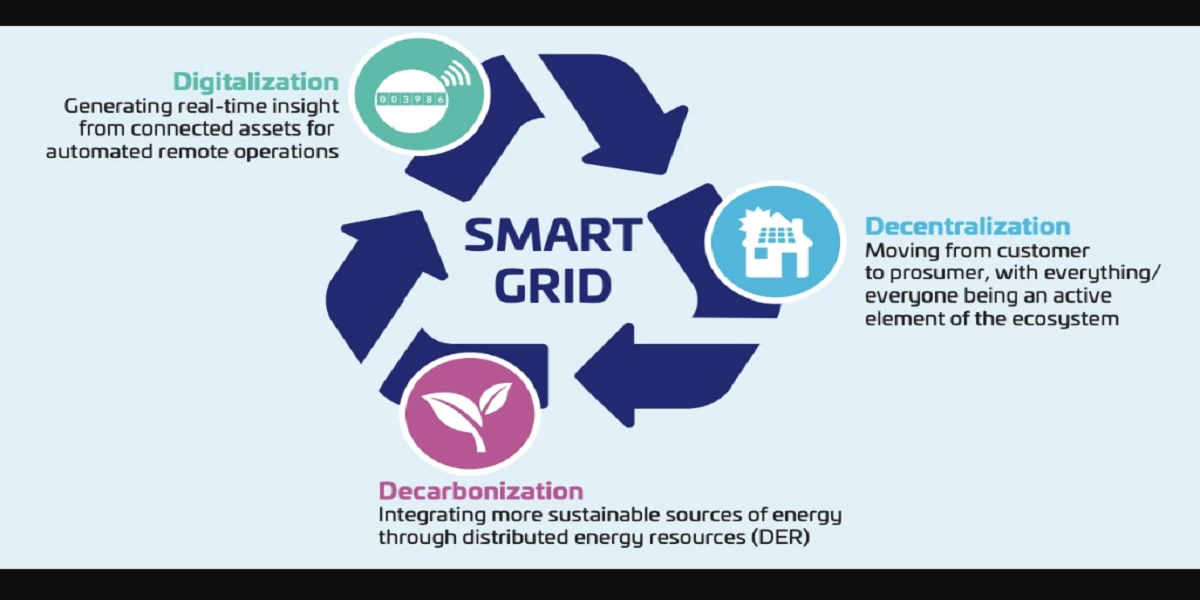
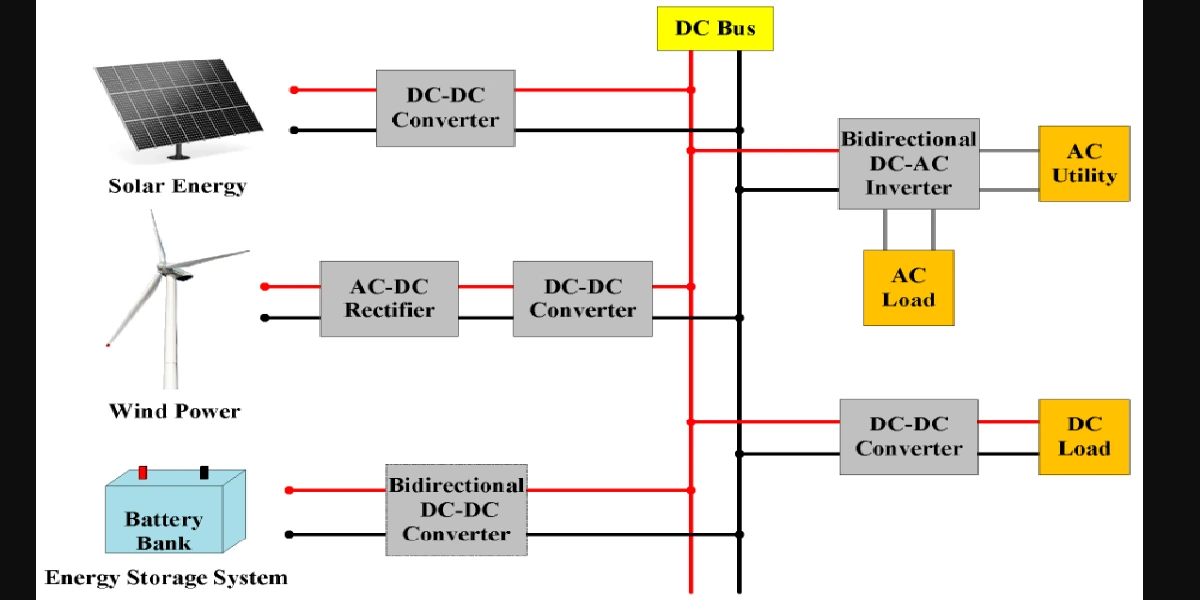
Generally signals are single valued functions of time that convey the information which may be real (or) complex valued. The main classifications of signals are as follows.
(i) Continuous – Time (CT) signals
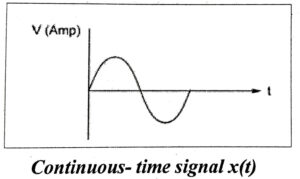
The signals that are defined for every instant of time or over a continuous range of time and is also called as an analog signal. They are denoted by x(t).
(ii) Discrete – Time (DT) signals
The signals that are defined at discrete (particular) instants of time are known as discrete – time signals. They are continuous in amplitude but discrete in time. They are denoted by x(n).
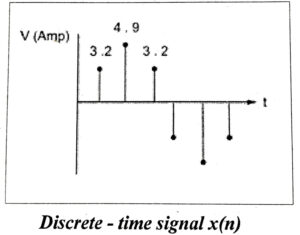
(iii) Digital signals
The signals that are discrete in time and quantized in amplitude are digital signals. An analog signal can be converted into a digital signal through sampling, quantizing (rounded off sample value) and coding processes.
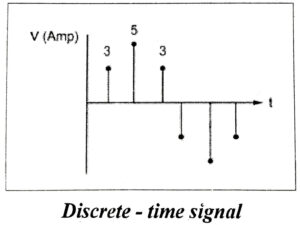
(iv) Random signals
A random signal is an unpredictable signal and is associated with a certain amount of uncertainty before it actually occurs.

| Read More Topics |
| General communication system |
| Basic types of communication systems |
| Introduction to operational amplifiers |