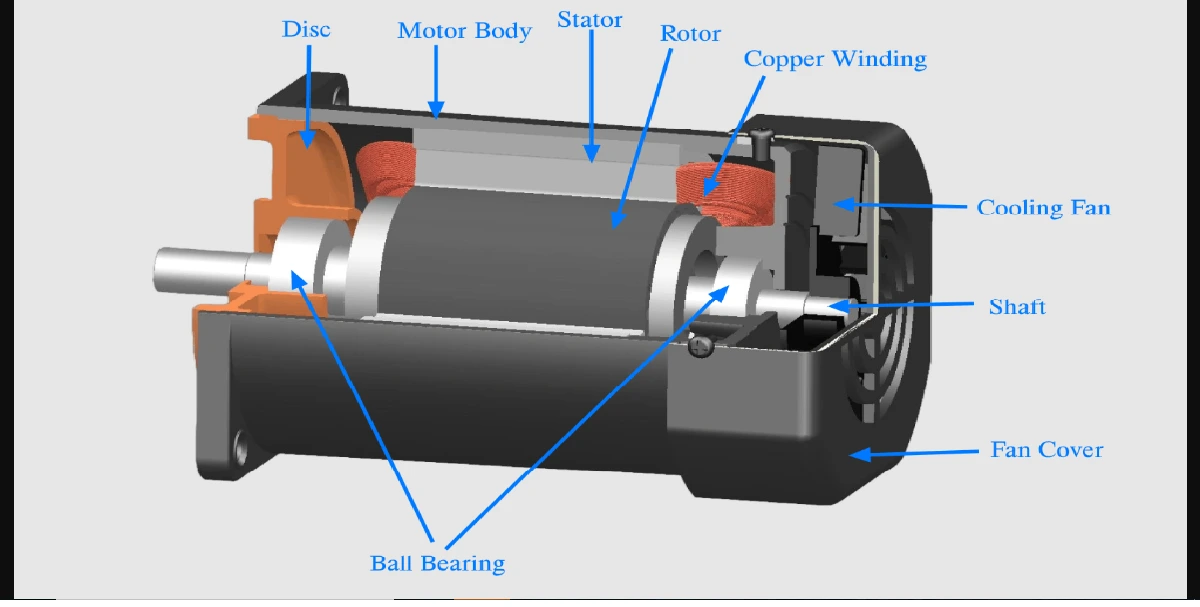
The unit of electric resistance is the ohm(Ω), where one ohm is one volt per ampere. It is defined as the resistance between two points in a conductor when a constant electric potential of one volt applied at the two points produces a current flow of one ampere in the conductor.
Thus, ![]()
where V is the potential difference across the two points, in volts, and I is the current flowing between the two points, in amperes.
The reciprocal of resistance is called conductance and is measured in siemens (S).
Thus, ![]()
where R is the resistance in ohms.
Find the conductance of a conductor of resistance: (a) 10 Ω (b) 5 kΩ (c) 100 mΩ.
(a) Conductance ![]()
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]()
| Read More Topics |
| Electrochemical energy storage |
| Points of consideration for etching process |
| Primary standard of luminous intensity |
| Power and signal transmission |