Modes of transfer
When the temperature of a body increases, the energy supplied to the body is being stored in the form of thermal or heat energy. In the normal process, the transmission of heat takes place from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature.
- conduction,
- convection and
- radiation
Conduction
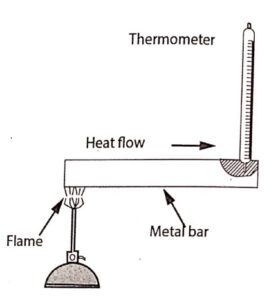
Fig 1.1 Process of conduction
This mode of transmission is possible in the case of solids, liquids and gas.
Convection
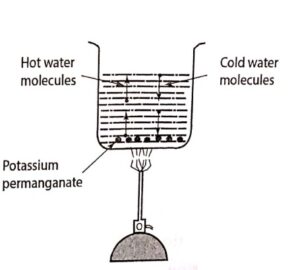
The water in the central portion at the bottom of beaker gets heated first. It rises up and the water from the top comes down along the sides to get heated. This upward and downward motion can be made visible by placing a crystal of potassium permanganate at the bottom of the beaker.
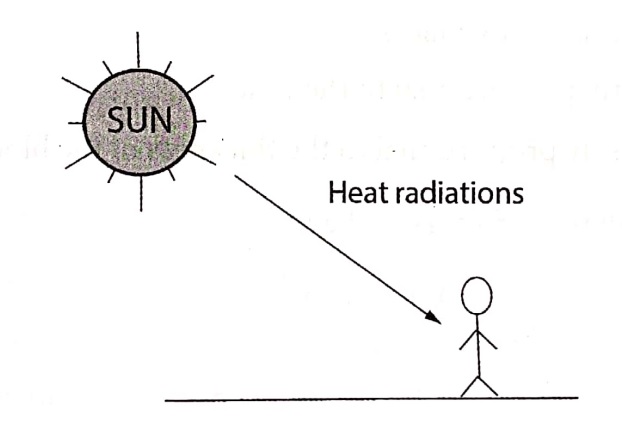
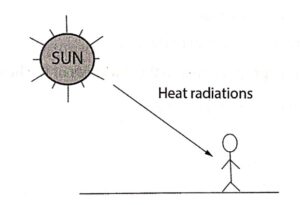
Radiation
It is the process in which heat is transmitted from one place to the other directly, without the agency of any material medium.
Example
Heat from the sun reaches us with an enormous velocity of light as shown in (Fig. 1.3). Through the sun is millions of miles away from the earth and there is no material medium for the greater part of the distance, the heat reaches us with the velocity of light. Thus heat radiations can pass through vacuum. The properties of heat radiations are similar to light radiation.
| Read More Topics |
| Linear flow of heat along a bar |
| Heat flow through a compound media or wall |
| De-Broglie’s concept of matter |