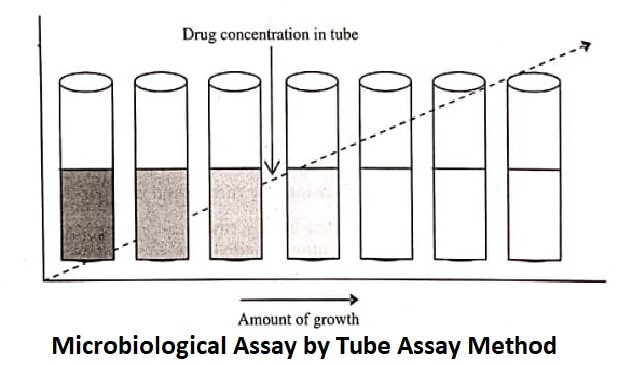
This method depends on the microbial culture growth in a uniform solution of antibiotic in a fluid medium favourable to its rapid growth in the absence of antibiotic. This method involves a shorter incubation period (4-5 hours) for the growth of test microorganism. However, this assay method is affected by the presence of solvent residues or other inhibitory substances. This method is not used for cloudy or turbid preparations.
The steps involved in turbidimetric method are given below:
- The standard solution is prepared in five different concentrations by diluting the stock solution for making the standard curve.
-
A median concentration is selected and the sample of test antibiotic solution is diluted up to this concentration.
-
1ml of each concentration of the standard and sample solutions is placed in each tube in duplicate.
- 9ml of nutrient medium inoculated with the test microorganism is added to each tube.
-
Simultaneously, three control tubes, one with the inoculated culture medium (culture control), second similar but treated with 0.5ml of dilute formaldehyde solution (blank), and third with un-inoculated culture medium are prepared.
-
All the tubes are incubated for 4-5 hours at the specified temperature.
-
0.5ml of dilute formaldehyde solution is added to each incubated tube.
-
By measuring the absorbance of each solution in the tubes against the blank at about 530 nm, the growth of test microorganism is determined (figure).
| Read More Topics |
| Methods of prevention of contamination |
| Factors influencing disinfection |
| Types of laminar airflow hood |
| Embryonated hen’s egg introduction |