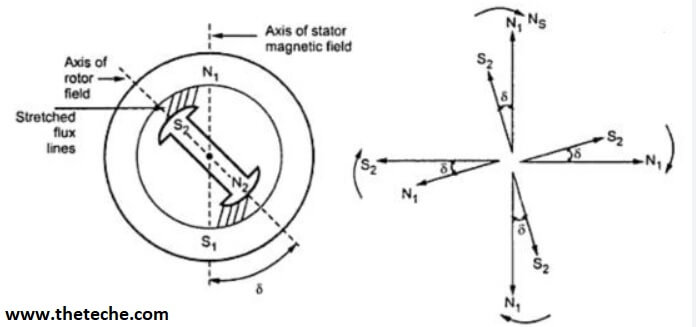
The four various types of torque associated with a synchronous motor are described below.
Four types of torque are,
Starting torque
- It indicates the ability of the motor to accelerate the load. It is also sometimes called “break away torque”.
- It may be as low as 10% in case of centrifugal pumps, and as high as “200 or 250% of full load torque”, as in case of loaded reciprocating two-cylinder compressors.
- The synchronous motor possesses no self starting torque; yet in modern synchronous motors, by making proper changes in the design of damper windings, almost any reasonable torque can be developed.
Running torque
- Running torque is the torque developed by the motor under running condition.
- It is determined by the output power and speed of the driven machine.
- Peak output power determines the maximum torque that would be required by the driven machine.
- The breakdown or maximum running torque of a motor must be greater than this value in order to avoid stalling of the machine.
Pull in torque
It pertains to the ability of the machine to pull in to synchronism when changing from induction to synchronous motor operation.
Pull out torque
It is the maximum torque that the synchronous motor will develop without pulling out of synchronism. Its value ranges from 1.25 to 3.5 times the full load torque.
Enlist the advantages and disadvantages of synchronous motor
| Advantages of Synchronous Motor | Disadvantages of Synchronous Motor |
| The speed is constant and independent of load. | It cannot be started under load. |
| These motors usually operate at higher efficiencies. | It requires dc excitation which must be supplied from external source. |
| Electro magnetic power varies linearly with the voltage. | It has a tendency to hunt. |
| These motors can be constructed with wider air gaps than induction motors, which make them better mechanically. | It cannot be used for variable speed jobs as there is no possibility of speed adjustment. |
| An Over excited synchronous motor having a leading power factor can be operated in parallel with induction motors. | Collector rings and brushes are required. |
| Read More Topics |
| Alternator Construction and Working |
| Pitch factor and distribution factor |
| Single phase induction motor |
| The microelectronics fabrication process flow |