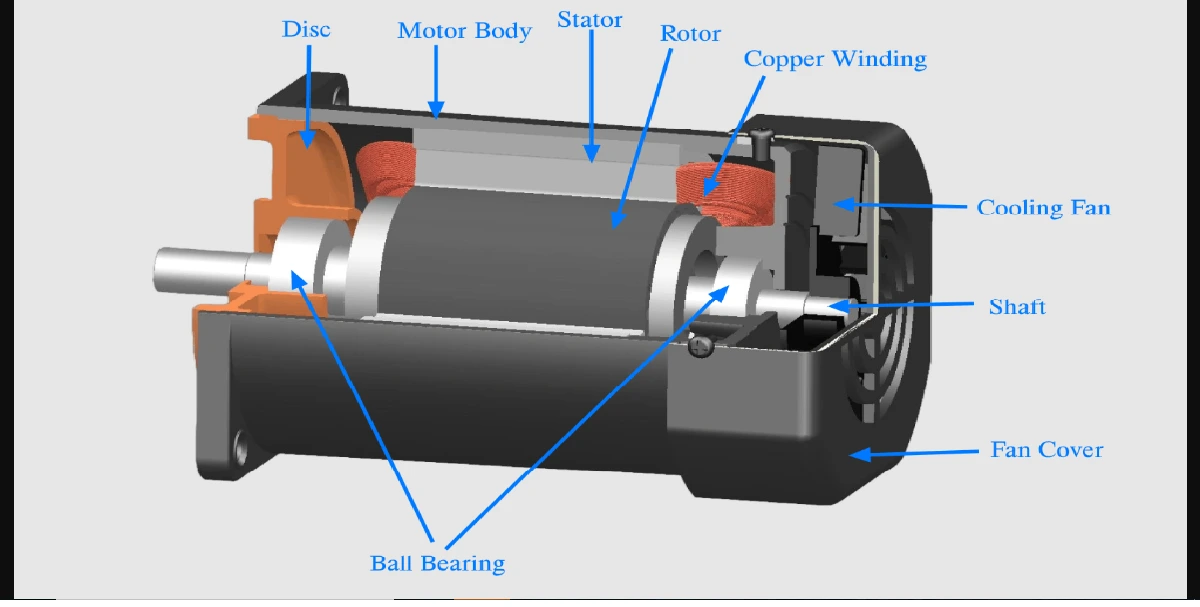
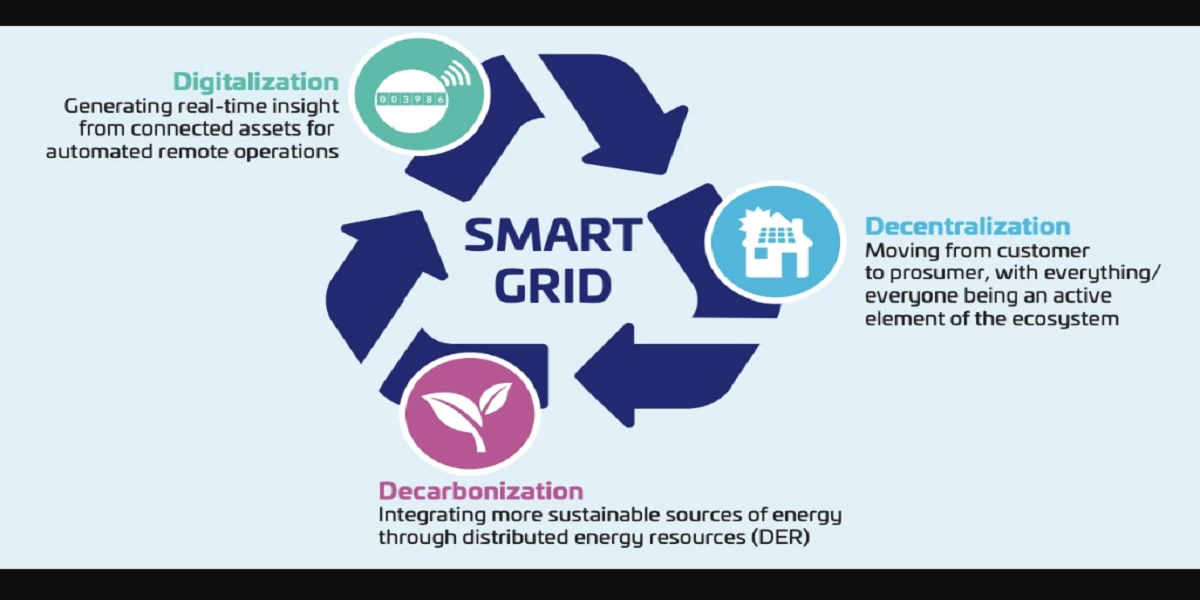
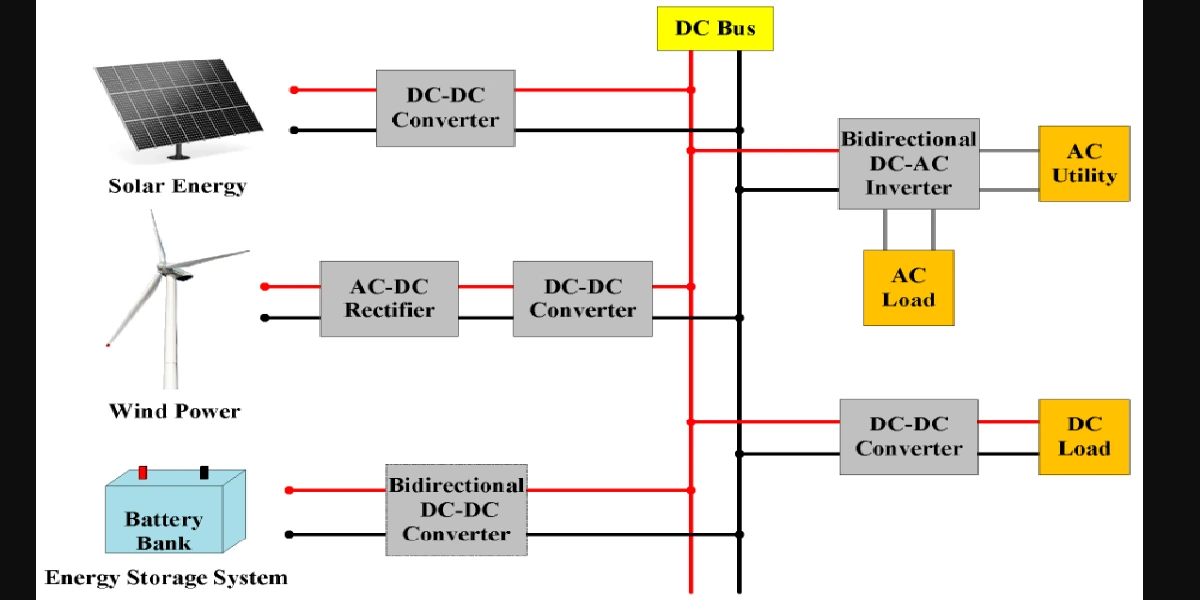
A power system consists of generation, transmission and distribution system. The components of the power systems are generators, transformers, transmission lines, distribution lines, loads and compensating devices like shunt, series, static VAR compensators.
In order to maintain power system, the bulk power has to be transmitted through transmission and distribution lines to the consumers safely and economically.
The evaluation of power system is called as power system analysis.
In monitoring power system analysis, we are mainly dealing with power or load flow analysis, short circuit analysis and stability analysis.
The functions of power system analysis are :
> To monitor the voltage at various buses, real and reactive power flow between buses.
> To design the circuit breakers.
> To plan future expansion of the existing system.
> To analyze the system under different fault conditions ( 3𝜙 fault, L-G, L- L, L-L-G faults).
> To study the ability of the system for large disturbances (sudden application of large load).
> To study the ability of the system for small disturbances (routine or small load changes).
The most important characteristic of the power system is that it can neither store energy nor is it the ultimate source of energy. The system only converts the energy available from natural sources into the electrical form and then handles it in an efficient manner.
The natural sources of energy are the following :
- Coal,
- Water flow,
- Uranium and thorium (Fissible materials),
- Fossil fuel (oil, natural gas),
- Wind,
- Tidal,
- Solar,
- Biogas, etc.
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h4″ img=”” question=”What is power system analysis?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] The evaluation of power system is called as power system analysis. [/sc_fs_faq]
| Read More Topics |
| Typical BJT characteristics and maximum ratings |
| Conduction in semiconductor materials |
| Introduction to electromagnetic induction |