Jigs and Fixtures – Locating and Clamping Principles
Jigs and fixtures are the devices which are mainly designed for holding, supporting and locating and clamping principles the workpieces and to guide the tools. By using “Jigs and Fixtures”, the cost of manufacture is reduced extensively. These devices are used to produce a repetitive type of workpieces with “zero defects”. But these are economical in mass production only. Jigs and fixtures are designed to save production time, to maintain dimensional accuracy, to facilitate quick and interchangeable assembly.
OBJECTIVES OF TOOL DESIGN
Tooling refers to the hardware necessary to produce a particular component. Tooling consist of a vast array of cutting devices, jigs, fixtures, dies and gauges used in normal production. The various types of tooling are:
- Cutting tools
- Single point cutting tools
- Multi-point cutting tools
- Press tools
- Dies
- Jigs and Fixtures
- Gauges
Tool design is the process of designing and developing the tools, methods, and techniques necessary to improve manufacturing efficiency and productivity. It depends on the following factors:
- Overall size and shape of the component to be manufactured
- Type and condition of work piece material.
- Method of machining operation and sequence of operations
- Degree of accuracy required.
- Number of components to be manufactured.
- Locating and clamping surfaces on the component.
- Type and size of machine tool: Whether the machine tool is single spindle or multi spindle.
- Should the tool be capable of performing more than one operation?
- Cutting tool materials.
- Life of cutting tool required.
- Cutting fluids to be used.
The main objectives of tool design are to lower the manufacturing cost while maintain the quality and increased production by cutting down time between machining operations. Various objectives of tool design are listed as follows:
- To provide simple, easy to operate tools for maximum efficiency.
- To reduce manufacturing expenses by producing parts at the lowest possible cost.
- To design tools, which consistently produce produce parts of high quality.
- To increase the rate of production with existing machine tools.
- To design tool to make it foolproof and to prevent improper use.
- To select materials that will give adequate tool life.
INTRODUCTION TO JIGS AND FIXTURES
Production devices are generally work holding devices, such as work holder with without tool guiding setting arrangement. These are generally called as jigs and fixtures.
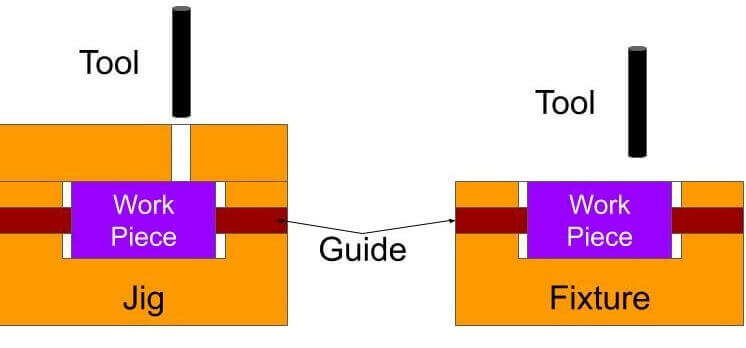
A jig may be defined as a work holding devices which locates and holds the component for a specific operation. It is also provided with tool guiding elements. They are usually lighter in construction and direct the tool to the correct position on the workpiece. It is rarely clamped on the machine table because it is necessary to move on the table to align the bushes in the jig with machine spindle. Jigs are used on drilling, reaming, trapping and counter boring operations.
A fixture may be defined as a work holding device which only holds and positions the workpiece. It does not guide the cutting tool. Sometimes, there is a provision in the fixture for setting the tool with respect to the work piece. Fixtures are the most often clamped to the machine table. Fixtures are used in turning, milling, grinding, shaping, planning and boring operations.
FUNCTIONS OF JIGS
Most of the industrial products produced may contain one or more holes. The significant of the hole may vary from place to place. Location, finishing and size of the holes may be critical in components of aircraft, missiles and automobile etc. Size and finishing of holes in few places such as, hole in a lock key to hang in key chain may not play significant role. Holes are produced in many ways such as drilling, boring, punching and gas cutting etc. Drilling is the most commonly used method in industries. Laying out the position of many numbers holes using try square, ruler, scriber and center punch may leads to inaccuracies. To eliminate the marking process and its associated errors and also to increase the rate of production, industrial practitioners are using jigs to drill, ream and tap the holes.
The following are the functions of a drill jig;
- To locate the hole in the appropriate positions
- To clamp the workpiece during drilling, reaming or tapping
- To guide the drills, reamers or tap into the proper position on the workpiece.
FUNCTIONS OF FIXTURES
Locating and clamping are the two important activities to ensure the desired quality in production related operations like machining, welding, inspection and assembly. When few parts are to be produced, many operations can be performed by clamping the workpiece to the machine table without using a specialized and dedicated work holding device. When number of parts produced increased significantly, much of the time spent on locating and clamping. Those times are nonproductive time, which will increase the manufacturing lead time. Fixture is a device used for locating and holding the workpiece during machining and positioning parts relative to each other during assembly and welding. Following are the functions of a fixture.
- To locate and position the workpiece relative to the cutting tool-+
- To clamp the workpiece during machining, welding, inspection or assembly
ADVANTAGES OF JIGS AND FIXTURES
The following are the advantages of using jigs and fixtures in mass production Industries.
- It reduces the production time by eliminating the marking out, measuring and setting the job.
- It reduces the cost of production by eliminating the laying out of work and setting up of tools.
- It increases the machining accuracy as the work is rigidly fixed and located and tool is guided.
- It minimizes the machining time by increasing depth of cut, feed and speed, due to better clamping rigidity of the job and guiding the tool.
- Interchangeability of manufacture is achieved by enabling the production of identical parts.
- It minimizes the assembly cost due to interchangeability and eliminating the operations, such as filing, etc.
- It reduces the operator’s fatigue, as the material handling is less.
- Semi-skilled operators are sufficient to perform the operations, as the setting of the tool and work is simple. Therefore, it also reduces the labour cost.
- It reduces the cost of inspection as the products are produced with very less defects.
- It minimizes the overall cost of production by partly or fully automatizing the process.
BASIC ELEMENTS OF JIGS AND FIXTURES
The various elements of jigs and fixtures are as follows;
- Locating elements:
Location refers to the establishment of a proper relationship between the workpiece and jig or fixture. Locating elements are used to position the workpiece accurately with respect to the tool guiding or setting elements in the fixture.
- Clamping elements:
The main purpose of clamping element is to extent a force to press the workpiece against the locating surfaces and holds it against the action of cutting forces.
- Tool guiding and setting elements:
Tool guiding elements are mainly useful to the jigs. In jigs, a hardened bushing is fastened to the sides of the jig to guide the tool to its proper position in the work. Tool setting elements are used in the fixtures where a target or set block is used to set the location of the tool with respect to the work piece within the fixtures.
PRINCIPLES OF JIGS AND FIXTURES DESIGN
The main considerations of jigs and fixture design are as follows.
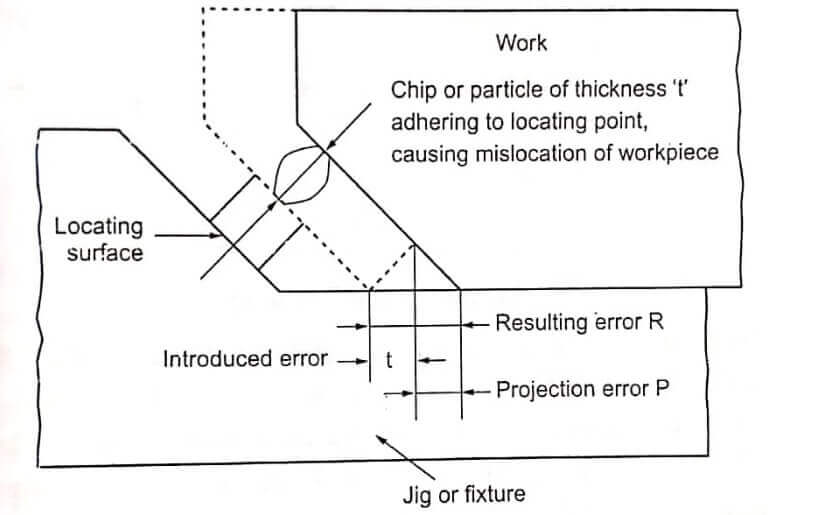
Location;
- Locating surfaces should be as small as possible and the location must be done from the machined surface.
- Sharp corners in the locating surfaces must be avoided.
- Locating pins should be easily accessible and visible to the operator
- Adjustable locators should be provided for rough surfaces.
Clamping;
- Clamping should always be arranged directly above the points supporting the work.
- Quick acting clamps should be used wherever possible.
- Clamps should not cause deformation of the workpiece.
- Position of clamps should provide the best resistance to the cutting tool.
- Cutting forces of the tool should act against the solid part of the jig and not against the clamps.
- All the clamps and adjustments should be on the sides.
- Clamps should allow rapid loading and unloading of the components.
Loading and unloading;
The loading and unloading process of the workpiece should be as easy as possible. Loading and supporting surfaces are usually made of hardened material and also it should be renewable wherever possible. Enough space should be left for hand movements between walls of a jig and workpiece.
Stability and Rigidity;
Jigs and fixtures should possess a high rigidity to withstand the cutting forces. At least, four legs should be provided on the jigs for the stability. The fixtures are rigidity fixed on the machine table. The equipment is made as rigid as necessary for the operation.
Clearance for Chips:
Adequate space in the form of channel ways should be provided to enable the metal chips to be blown clear easily.
Fool Proof Design;
Jigs and fixtures should be fool proof besides being safe to use. The design of jigs and fixture is such that it is impossible to use the workpiece and tool in any position other than the correct one. Locating pins are provided for this purpose.
Provision for Tool Guides;
Provision for tool guides in jig bushing and cutter setting devices in fixtures should be made.
Provision for indexing:
The provision for indexing the workpiece should be made wherever it is necessary. It enables the workpiece to divide into many numbers of equi spaced faces.
Weight:
Jigs and fixtures should be lighter in weight. Jig weight should be kept below 15kg since they are to be handled often.
Safety:
Jigs and fixtures are designed for safety. Handles and levers should be large enough. All sharp edges should be removed or avoided.
Coolant supply:
Adequate arrangements must be made for the apply of coolant to the cutting edges for reducing the friction.
Economy:
Jig and fixture should reduce machining and production costs by providing case of manufacturing.
ESSENTIAL FEATURES OF JIGS OR FIXTURES
Any jig or fixture should satisfy the following conditions before putting into use.;’
Reduction of idle time:
During loading and unloading of components, locating and clamping of components, and time spent due to hazardous situation, the machine will be idle or at rest. To perform the required operations within a shorter period of time, the above-mentioned time has to be reduced.
Rigidity and stability:
Jigs and fixtures should be high enough rigid and stable. Then only, it can withstand all cutting forces in the form of vibrations while working period.
Safety:
The jigs and fixtures should be designed to avoid any injury to operator while working. Due to this, sharp corners should be avoided by providing blended edges.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN JIGS AND FIXTURES
| S.No | Jigs | Fixtures |
| 1. | It holds, locates the workpiece and also guides the tool. | It holds and positions the workpiece but does not guide the tool. |
| 2. | Jigs are smaller in size and lighter in construction. | Fixtures are usually massive and heavier in construction. |
| 3. | Semi-skilled workers can operate. | Skilled operator is necessary as compared to jig. |
| 4. | Fabrication time and cost are less | Production time and cost are more. |
| 5. | Clamping with the table is often not necessary. | It is bolted rigidly on the machine table. |
| Read More Topics |
| Types of casting process |
| NC Machine tool fixture |
| Bend test for steel |